阅读更多
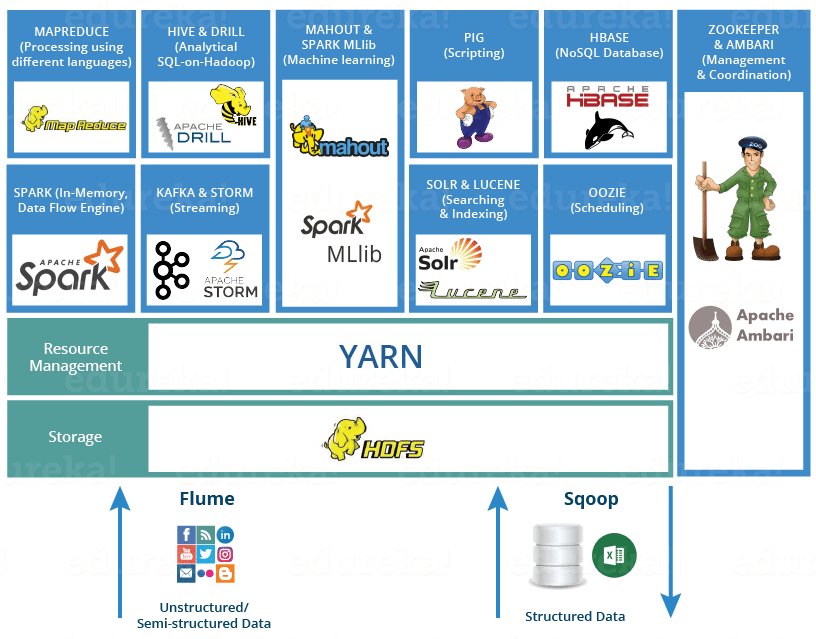
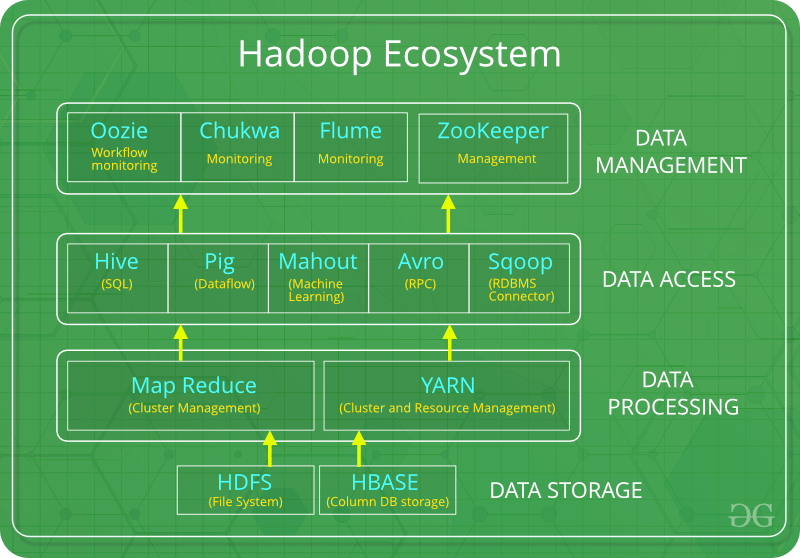
Below are the Hadoop components, that together form a Hadoop ecosystem:
HDFS -> Hadoop Distributed File SystemYARN -> Yet Another Resource NegotiatorMapReduce -> Data processing using programmingSpark -> In-memory Data ProcessingPIG -> Data Processing Services using Query (SQL-like)HBase -> NoSQL DatabaseMahout & Spark MLlib -> Machine LearningDrill -> SQL on HadoopZookeeper -> Managing ClusterOozie -> Job SchedulingFlume -> Data Ingesting ServicesSolr & Lucene -> Searching & IndexingAmbari -> Provision, Monitor and Maintain cluster
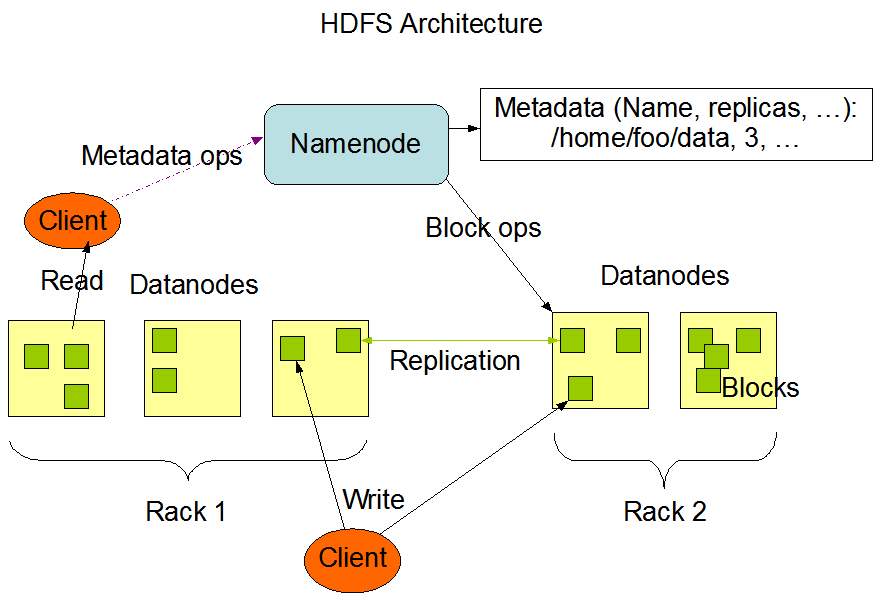
HDFS has a master/slave architecture. An HDFS cluster consists of a single NameNode, a master server that manages the file system namespace and regulates access to files by clients. In addition, there are a number of DataNodes, usually one per node in the cluster, which manage storage attached to the nodes that they run on. HDFS exposes a file system namespace and allows user data to be stored in files. Internally, a file is split into one or more blocks and these blocks are stored in a set of DataNodes. The NameNode executes file system namespace operations like opening, closing, and renaming files and directories. It also determines the mapping of blocks to DataNodes. The DataNodes are responsible for serving read and write requests from the file system’s clients. The DataNodes also perform block creation, deletion, and replication upon instruction from the NameNode.
Import paths of docker:
/var/log/hadoop
/var/log/hadoop/hadoop-hadoop-namenode-$(hostname).out/var/log/hadoop/hadoop-hadoop-datanode-$(hostname).out/var/log/hadoop/hadoop-hadoop-resourcemanager-$(hostname).out/var/log/hadoop/hadoop-hadoop-nodemanager-$(hostname).outuserlogs: Logs for applications that are submitted to yarn.
Important ports:
8020: The NameNode’s default RPC port is 8020.9866: The datanode server address and port for data transfer.8042: NodeManager (Web UI).8088: ResourceManager (Web UI).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 SHARED_NS=hadoop-ns HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME=hadoop docker run -dit --name ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} --hostname ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} --network ${SHARED_NS} --privileged \ -p 127.0.0.1:8020:8020 \ -p 127.0.0.1:9866:9866 \ -p 127.0.0.1:8042:8042 \ -p 127.0.0.1:8088:8088 \ apache/hadoop:3.3.6 bash docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "cat > /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml << EOF <configuration> <property> <name>fs.defaultFS</name> <value>hdfs://${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :8020</value> </property> </configuration> EOF" docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "cat > /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml << EOF <configuration> <property> <name>dfs.replication</name> <value>1</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.permissions.enabled</name> <value>false</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name> <value>/opt/hadoop/data</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.address</name> <value>${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :9866</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.http.address</name> <value>${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :9864</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.ipc.address</name> <value>${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :9867</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.hostname</name> <value>${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} </value> </property> </configuration> EOF" docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "cat > /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml << EOF <configuration> <property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.hostname</name> <value>${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} </value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name> <value>mapreduce_shuffle</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb</name> <value>8192</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores</name> <value>4</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb</name> <value>1024</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb</name> <value>8192</value> </property> </configuration> EOF" docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "cat > /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml << EOF <configuration> <property> <name>mapreduce.framework.name</name> <value>yarn</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.app.mapreduce.am.env</name> <value>HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=/opt/hadoop</value> </property> <property> <name>mapreduce.map.env</name> <value>HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=/opt/hadoop</value> </property> <property> <name>mapreduce.reduce.env</name> <value>HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=/opt/hadoop</value> </property> <property> <name>mapreduce.application.classpath</name> <value>/opt/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/*,/opt/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/lib/*</value> </property> </configuration> EOF" docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'hdfs namenode -format' docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'mkdir -p /opt/hadoop/data' docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'hdfs --daemon stop namenode; hdfs --daemon start namenode' docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'hdfs --daemon stop datanode; hdfs --daemon start datanode' docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'yarn --daemon stop resourcemanager; yarn --daemon start resourcemanager' docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'yarn --daemon stop nodemanager; yarn --daemon start nodemanager' docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'mapred --daemon stop historyserver; mapred --daemon start historyserver' docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'hdfs dfsadmin -report'
Test:
1 docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'hadoop jar /opt/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-*.jar pi 10 100'
Step
Initiator
Receiver
Description
①
CLIENT
AS
Requests initial ticket (TGT)
②
AS
CLIENT
Returns encrypted TGT and session key
③
CLIENT
TGS
Requests service ticket using TGT
④
TGS
CLIENT
Returns encrypted service ticket and session key
⑤
CLIENT
SERVICE
Uses service ticket to request access
⑥
SERVICE
CLIENT
Optional mutual authentication response
Concepts:
Key Distribution Center, KDC
The central server responsible for managing authentication.
Comprises two sub-components:
Authentication Server (AS): Authenticates the client and issues the Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT).
Ticket Granting Server (TGS): Issues service-specific tickets upon request.
Principal: A unique identity (user, service, or host) in the Kerberos system, e.g., user@REALM or service/hostname@REALM.
Realm: A logical network served by a single KDC, identified by an uppercase string, e.g., EXAMPLE.COM.
Keytab: A file storing pre-shared credentials for a user or service, used for automated authentication.
Ticket: A temporary set of credentials that allows a principal to authenticate to services.
Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT): Issued by the AS, used to request service tickets.
Service Ticket: Allows access to a specific service.
Kerberos Commands:
kinit <principal>[@<kerberos_realm>]: Login with password.
kinit -c <cache_path> <principal>[@<kerberos_realm>]: Login with password and specific cache path.
kinit -kt <keytabpath> <principal>[@<kerberos_realm>]: Login with keytab.
kinit -kt <keytabpath> -c <cache_path> <principal>[@<kerberos_realm>]: Login with keytab and specific cache path.
klist: Display credentials cache.klist -c <cache_path>: Display specifies credentials cache.klist -e -d -k -t -K <keytabpath>: Display keytab information.kdestroy: Destroy credentials cache.kdestroy -c <cache_path>: Destroy specifies credentials cache.Environments:
export KRB5_TRACE=/dev/stdout: For debug.export KRB5_CONFIG=<path/to/krb5.conf>: Specify the config file, parse logic domain to real domain.export KRB5CCNAME=FILE:/tmp/krb5cc_testuser: Use local file as cache.export KRB5CCNAME=MEMORY:: Use meory as cache.
kadmin.local Commands:
Tips:
Make sure target user has permission to read related files, including config, TGT, keyTab etc.
Prepare ubuntu image with kerberos dependencies
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 mkdir -p /tmp/ubuntu-with-kerberoscat > /tmp/ubuntu-with-kerberos/Dockerfile << 'EOF' FROM ubuntu:xenial RUN apt update && \ DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt install -y ntp python-dev python-pip python-wheel python-setuptools python-pkg-resources krb5-admin-server krb5-kdc && \ apt install -y vim iputils-ping iproute2 EOF docker build -t ubuntu:xenial_with_kerberos /tmp/ubuntu-with-kerberos
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 SHARED_NS=hadoop-ns HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME=hadoop-with-kerberos KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME=kerberos REAL_DOMAIN=liuyehcf.org HADOOP_HOSTNAME=${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} .${REAL_DOMAIN} KERBEROS_HOSTNAME=${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} .${REAL_DOMAIN} KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN=example.com KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER=$(echo ${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN} | tr "[:lower:]" "[:upper:]" ) docker run -dit --name ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} --hostname ${KERBEROS_HOSTNAME} --network ${SHARED_NS} --privileged \ -p 127.0.0.1:88:88/tcp -p 127.0.0.1:88:88/udp \ -p 127.0.0.1:464:464/tcp -p 127.0.0.1:464:464/udp \ -p 127.0.0.1:749:749/tcp -p 127.0.0.1:749:749/udp \ ubuntu:xenial_with_kerberos docker exec ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "tee /etc/krb5.conf > /dev/null << EOF [libdefaults] default_realm = ${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} dns_lookup_realm = false dns_lookup_kdc = false ticket_lifetime = 24h renew_lifetime = 7d forwardable = true [realms] ${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} = { kdc = ${KERBEROS_HOSTNAME} admin_server = ${KERBEROS_HOSTNAME} } [domain_realm] ${REAL_DOMAIN} = ${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} .${REAL_DOMAIN} = ${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} EOF" docker exec ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "cat > /etc/krb5kdc/kdc.conf << EOF [kdcdefaults] kdc_ports = 88 kdc_tcp_ports = 88 [realms] ${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} = { database_name = /var/lib/krb5kdc/principal admin_keytab = /etc/krb5kdc/kadm5.keytab acl_file = /etc/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl key_stash_file = /etc/krb5kdc/stash log_file = /var/log/krb5kdc.log kdc_ports = 88 max_life = 10h 0m 0s max_renewable_life = 7d 0h 0m 0s } EOF" docker exec ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "cat > /etc/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl << EOF */admin@${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} * EOF" docker exec ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'kdb5_util create -s <<EOF !Abcd1234 !Abcd1234 EOF' docker exec ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c '/usr/sbin/krb5kdc' docker exec ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c '/usr/sbin/kadmind' docker exec ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'mkdir -p /etc/security/keytabs' docker exec ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "kadmin.local <<EOF addprinc -randkey nn/${HADOOP_HOSTNAME} @${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} addprinc -randkey dn/${HADOOP_HOSTNAME} @${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} listprincs ktadd -k /etc/security/keytabs/nn.service.keytab nn/${HADOOP_HOSTNAME} @${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} ktadd -k /etc/security/keytabs/dn.service.keytab dn/${HADOOP_HOSTNAME} @${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} quit EOF" docker exec ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "kadmin.local <<EOF addprinc -pw 123456 user_with_password@${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} listprincs quit EOF" docker exec ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "kadmin.local <<EOF addprinc -randkey user_with_keytab@${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} ktadd -k /etc/security/keytabs/user_with_keytab.service.keytab user_with_keytab@${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} listprincs quit EOF"
Test:
Test user_with_password
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 kinit user_with_password klist docker cp ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} :/etc/krb5.conf ~/.krb5.conf sudo sed -i "/127.0.0.1 ${KERBEROS_HOSTNAME} /d" /etc/hosts echo "127.0.0.1 ${KERBEROS_HOSTNAME} " | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts > /dev/nullexport KRB5_CONFIG=~/.krb5.confkinit user_with_password klist
Test user_with_keytab
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 kinit -kt /etc/security/keytabs/user_with_keytab.service.keytab user_with_keytab klist docker cp ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} :/etc/krb5.conf ~/.krb5.conf sudo sed -i "/127.0.0.1 ${KERBEROS_HOSTNAME} /d" /etc/hosts echo "127.0.0.1 ${KERBEROS_HOSTNAME} " | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts > /dev/nulldocker cp ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} :/etc/security/keytabs/user_with_keytab.service.keytab ~/.user_with_keytab.service.keytab export KRB5_CONFIG=~/.krb5.confkinit -kt ~/.user_with_keytab.service.keytab user_with_keytab klist
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 SHARED_NS=hadoop-ns HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME=hadoop-with-kerberos KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME=kerberos REAL_DOMAIN=liuyehcf.org HADOOP_HOSTNAME=${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} .${REAL_DOMAIN} KERBEROS_HOSTNAME=${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} .${REAL_DOMAIN} KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN=example.com KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER=$(echo ${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN} | tr "[:lower:]" "[:upper:]" ) docker run -dit --name ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} --hostname ${HADOOP_HOSTNAME} --network ${SHARED_NS} --privileged \ -p 127.0.0.1:8020:8020 \ -p 127.0.0.1:9866:9866 \ apache/hadoop:3.3.6 bash docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "cat > /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml << EOF <configuration> <property> <name>fs.defaultFS</name> <value>hdfs://${HADOOP_HOSTNAME} :8020</value> </property> <property> <name>hadoop.security.authentication</name> <value>kerberos</value> </property> <property> <name>hadoop.security.authorization</name> <value>true</value> </property> </configuration> EOF" docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "cat > /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml << EOF <configuration> <property> <name>dfs.replication</name> <value>1</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.permissions.enabled</name> <value>false</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name> <value>/opt/hadoop/data</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.address</name> <value>${HADOOP_HOSTNAME} :9866</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.http.address</name> <value>${HADOOP_HOSTNAME} :9864</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.ipc.address</name> <value>${HADOOP_HOSTNAME} :9867</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.hostname</name> <value>${HADOOP_HOSTNAME} </value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.namenode.kerberos.principal</name> <value>nn/_HOST@${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} </value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.namenode.keytab.file</name> <value>/etc/security/keytabs/nn.service.keytab</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.kerberos.principal</name> <value>dn/_HOST@${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} </value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.keytab.file</name> <value>/etc/security/keytabs/dn.service.keytab</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.block.access.token.enable</name> <value>true</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.block.access.token.master.key.num</name> <value>2</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.block.access.token.lifetime</name> <value>600</value> </property> <property> <name>ignore.secure.ports.for.testing</name> <value>true</value> </property> </configuration> EOF" docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "sudo tee /etc/krb5.conf > /dev/null << EOF [libdefaults] default_realm = ${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} dns_lookup_realm = false dns_lookup_kdc = false ticket_lifetime = 24h renew_lifetime = 7d forwardable = true [realms] ${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} = { kdc = ${KERBEROS_HOSTNAME} admin_server = ${KERBEROS_HOSTNAME} } [domain_realm] ${REAL_DOMAIN} = ${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} .${REAL_DOMAIN} = ${KERBEROS_LOGIC_DOMAIN_UPPER} EOF" docker cp ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} :/etc/security/keytabs/nn.service.keytab /tmp/nn.service.keytab docker cp ${KERBEROS_CONTAINER_NAME} :/etc/security/keytabs/dn.service.keytab /tmp/dn.service.keytab docker cp /tmp/nn.service.keytab ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :/etc/security/keytabs/nn.service.keytab docker cp /tmp/dn.service.keytab ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :/etc/security/keytabs/dn.service.keytab docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'sudo chmod 644 /etc/security/keytabs/nn.service.keytab' docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'sudo chmod 644 /etc/security/keytabs/dn.service.keytab' docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'hdfs namenode -format' docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'sudo mkdir -p /opt/hadoop/data' docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'hdfs --daemon stop namenode; hdfs --daemon start namenode' docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'HDFS_DATANODE_SECURE_USER=root; \ JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/jre; \ sudo -E /opt/hadoop/bin/hdfs --daemon stop datanode; \ sudo -E /opt/hadoop/bin/hdfs --daemon start datanode' docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "kinit user_with_password <<EOF 123456 EOF" docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'hdfs dfsadmin -report'
Key points:
Directory /opt/hadoop/data must can be accessed by the user started datanode.
Credential file /etc/security/keytabs/dn.service.keytab must can be accessed by the user started datanode.
If ignore.secure.ports.for.testing is set to false, then the http port and tcp port must be smaller than 1023, otherwise it cannot pass the check.
Test:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c "cat > /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml << EOF <configuration> <property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.principal</name> <value>dn/_HOST@EXAMPLE.COM</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.keytab</name> <value>/etc/security/keytabs/dn.service.keytab</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.principal</name> <value>dn/_HOST@EXAMPLE.COM</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.keytab</name> <value>/etc/security/keytabs/dn.service.keytab</value> </property> </configuration> EOF" docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'hadoop jar /opt/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-*.jar pi 10 100'
core-site.xml
Path: $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml
Description: Contains configuration settings for Hadoop’s core system, including the default filesystem URI.
core-default.xml
hdfs-site.xml
Path: $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml
Description: Contains configuration settings specific to HDFS.
hdfs-default.xml
yarn-site.xml
Path: $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml
Description: Contains configuration settings for YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator).
yarn-default.xml
mapred-site.xml
Path: $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml
Description: Contains configuration settings specific to MapReduce.
mapred-default.xml
hadoop-env.sh
Path: $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh
Description: Sets environment variables for Hadoop processes, such as JAVA_HOME.
yarn-env.sh
Path: $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/yarn-env.sh
Description: Sets environment variables for YARN.
log4j.properties
Path: $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/log4j.properties
Description: Configures logging for Hadoop.
core-site.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 <configuration > <property > <name > fs.defaultFS</name > <value > hdfs://mycluster</value > </property > </configuration >
hdfs-site.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 <configuration > <property > <name > dfs.nameservices</name > <value > mycluster</value > </property > <property > <name > dfs.ha.namenodes.mycluster</name > <value > p0,p1,p2</value > </property > <property > <name > dfs.namenode.rpc-address.mycluster.p0</name > <value > 192.168.0.1:12000</value > </property > <property > <name > dfs.namenode.rpc-address.mycluster.p1</name > <value > 192.168.0.2:12000</value > </property > <property > <name > dfs.namenode.rpc-address.mycluster.p2</name > <value > 192.168.0.3:12000</value > </property > <property > <name > dfs.client.failover.proxy.provider.mycluster</name > <value > org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.ha.ConfiguredFailoverProxyProvider</value > </property > <property > <name > dfs.ha.automatic-failover.enabled.mycluster</name > <value > true</value > </property > </configuration >
FileSystem::CACHE will cache filesystem object, cache key is built from uri and Configuration, if you only modify hdfs-site.xml file itself, the object Configuration will be exactly the same, so comes with the cache hit.
How to disable it?, set property fs.<protocol>.impl.disable.cache to true in hdfs-site.xml
For hdfs, the property name is: fs.hdfs.impl.disable.cache
dfs.client.hedged.read.threadpool.sizedfs.client.hedged.read.threshold.millis
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 hdfs --daemon stop namenode hdfs --daemon stop datanode yarn --daemon stop resourcemanager yarn --daemon stop nodemanager mapred --daemon stop historyserver hdfs --daemon start namenode hdfs --daemon start datanode yarn --daemon start resourcemanager yarn --daemon start nodemanager mapred --daemon start historyserver
1 2 hdfs fsck <path> hdfs fsck <path> -files -blocks -replication
1 2 3 4 5 hdfs dfs -cat <path> hdfs dfs -text <path.avro>
1 2 3 hdfs dfs -setfacl -R -m user:hive:rwx / hdfs dfs -setfacl -R -m default:user:hive:rwx / hdfs dfs -getfacl /
1 2 yarn node -list yarn node -list -showDetails
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 yarn application -list yarn application -list -appStates ALL yarn application -status <appid> yarn logs -applicationId <appid> yarn application -kill <appid>
For linux, there are two ways of approaching this:
Access hadoop via container’s ip.
For mac with m chip, the above methods cannot work, because there will be an extra virtualization layer between mac and the container. Here are steps of how we can access hadoop in this situation:
We can use hostname to access both namenode and datanode, the hostname must be resolved in both container and Mac, and the container’s name should be the best solution.
Set port mapping for namenode’s port (8020 bydefault) and datanode’s port (9866 by default).
Update /etc/hosts, mapping hadoop’s container’s name to 127.0.0.1.
Config dfs.datanode.hostname at hadoop side (i.e. Container side), set its value to container’s name.
Config dfs.client.use.datanode.hostname to true at the client side (i.e. Mac side), otherwise it will use container’s ip address, which is unconnected between mac and container because of the extra virtualization layer.
Access hadoop via container’s name.
You need to implement the parsing of the path yourself.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public static void main (String[] args) { Configuration hadoopConf = new Configuration (); String hadoopConfDir = System.getenv(HADOOP_CONF_ENV); if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(hadoopConfDir)) { addHadoopConfIfFound(hadoopConf, hadoopConfDir); } } private static void addHadoopConfIfFound (Configuration configuration, String possibleHadoopConfPath) { if (new File (possibleHadoopConfPath).exists()) { if (new File (possibleHadoopConfPath + "/core-site.xml" ).exists()) { configuration.addResource( new org .apache.hadoop.fs.Path(possibleHadoopConfPath + "/core-site.xml" )); LOGGER.debug("Adding {}/core-site.xml to hadoop configuration" , possibleHadoopConfPath); } if (new File (possibleHadoopConfPath + "/hdfs-site.xml" ).exists()) { configuration.addResource( new org .apache.hadoop.fs.Path(possibleHadoopConfPath + "/hdfs-site.xml" )); LOGGER.debug("Adding {}/hdfs-site.xml to hadoop configuration" , possibleHadoopConfPath); } } }
What Is Apache Spark?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #!/bin/bash ROOT=$(dirname "$0 " ) ROOT=$(cd "$ROOT " ; pwd ) wget https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/apache/spark/spark-3.5.1/spark-3.5.1-bin-hadoop3.tgz tar -zxf spark-3.5.1-bin-hadoop3.tgz export SPARK_HOME=${ROOT} /spark-3.5.1-bin-hadoop3cat > ${SPARK_HOME} /conf/spark-env.sh << 'EOF' SPARK_MASTER_HOST=localhost EOF ${SPARK_HOME} /sbin/start-master.sh${SPARK_HOME} /sbin/start-worker.sh spark://127.0.0.1:7077
Stop:
1 2 ${SPARK_HOME} /sbin/stop-master.sh${SPARK_HOME} /sbin/stop-worker.sh
Test:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ${SPARK_HOME} /bin/spark-shellscala> val nums = sc.parallelize(1 to 10) scala> println(nums.count()) scala> :quit ${SPARK_HOME} /bin/spark-submit ${SPARK_HOME} /examples/src/main/python/pi.py 10
1 2 3 4 5 show catalogs;set catalog < catalog_name> ;show databases;use < database_name> ;
1 2 spark-shell --packages org.apache.spark:spark-avro_2.12:3.5.2
1 2 spark.read.format("parquet" ).load("hdfs://192.168.64.2/user/iceberg/demo/db/table/data/00000-0-e424d965-50e8-4f61-abc7-6e6c117876f4-0-00001.parquet" ).show(truncate =false ) spark.read.format("avro" ).load("hdfs://192.168.64.2/user/iceberg/demo/demo_namespace/demo_table/metadata/snap-2052751058123365495-1-7a31848a-3e5f-43c7-886a-0a8d5f6c8ed7.avro" ).show(truncate =false )
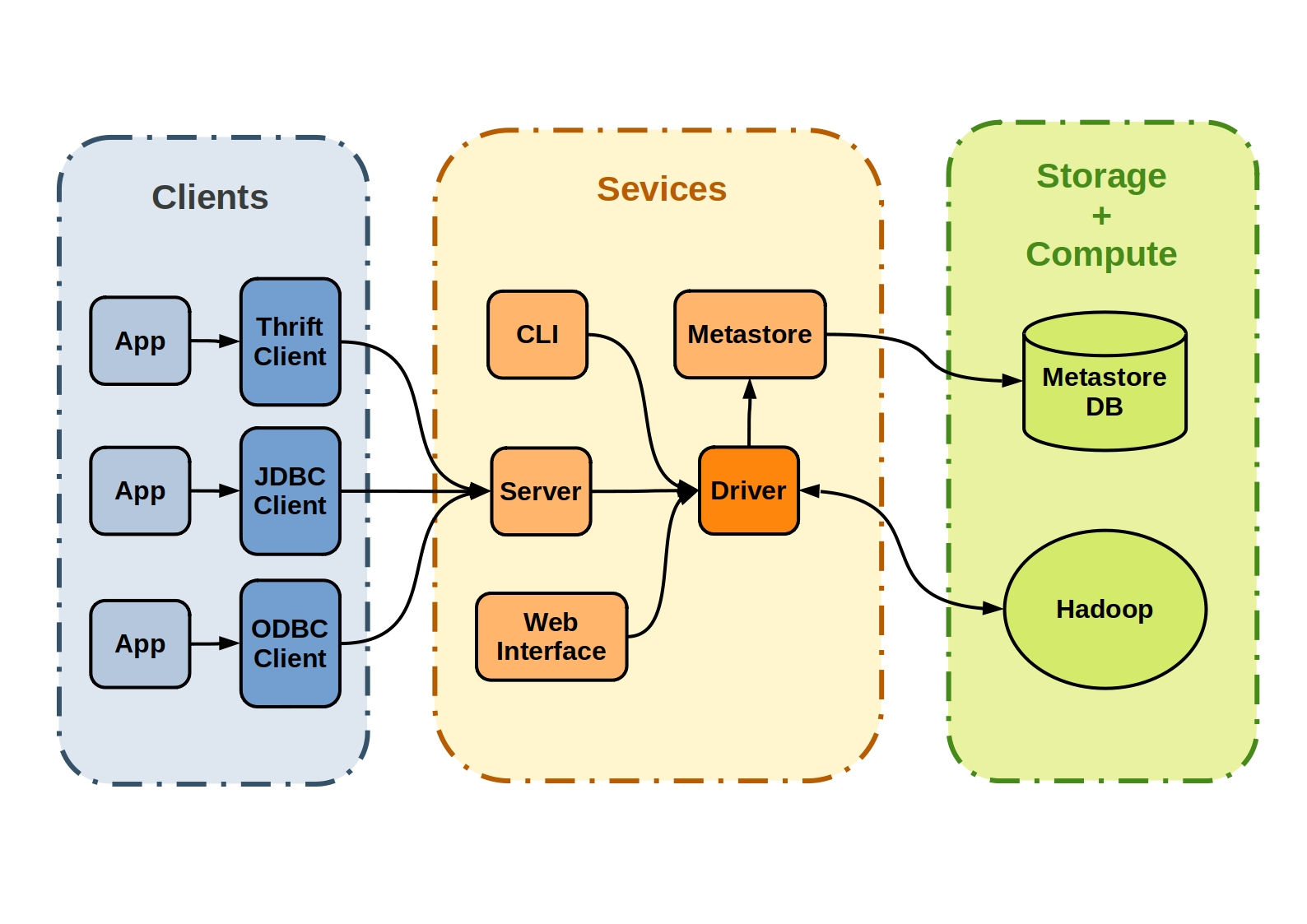
What is Apache Hive?
HS2 supports multi-client concurrency and authentication. It is designed to provide better support for open API clients like JDBC and ODBC.
The Hive Metastore (HMS) is a central repository of metadata for Hive tables and partitions in a relational database, and provides clients (including Hive, Impala and Spark) access to this information using the metastore service API. It has become a building block for data lakes that utilize the diverse world of open-source software, such as Apache Spark and Presto. In fact, a whole ecosystem of tools, open-source and otherwise, are built around the Hive Metastore, some of which this diagram illustrates.
Here is a summary of the compatible versions of Apache Hive and Hadoop (refer to Apache Hive Download for details):
Hive 4.0.0: Works with Hadoop 3.3.6, Tez 0.10.3
Issues:
Apache Hive - Quickstart
Start a hive container joining the shared network.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 SHARED_NS=hadoop-ns HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME=hadoop HIVE_PREFIX=hive-with-derby HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME=${HIVE_PREFIX} -metastore HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME=${HIVE_PREFIX} -server if [ ! -e /tmp/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin.tar.gz ]; then wget -O /tmp/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin.tar.gz https://downloads.apache.org/tez/0.10.3/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin.tar.gz fi docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'mkdir -p /opt/tez' docker cp /tmp/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin.tar.gz ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/tez docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c ' if ! hdfs dfs -ls /opt/tez/tez.tar.gz > /dev/null 2>&1; then rm -rf /opt/tez/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin tar -zxf /opt/tez/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin.tar.gz -C /opt/tez hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /opt/tez hdfs dfs -put -f /opt/tez/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin/share/tez.tar.gz /opt/tez fi ' HIVE_SITE_CONFIG_COMMON=$(cat << EOF <property> <name>hive.server2.enable.doAs</name> <value>false</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.tez.exec.inplace.progress</name> <value>false</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.exec.scratchdir</name> <value>/opt/${HIVE_PREFIX}/scratch_dir</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.user.install.directory</name> <value>/opt/${HIVE_PREFIX}/install_dir</value> </property> <property> <name>tez.runtime.optimize.local.fetch</name> <value>true</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.exec.submit.local.task.via.child</name> <value>false</value> </property> <property> <name>mapreduce.framework.name</name> <value>yarn</value> </property> <property> <name>tez.local.mode</name> <value>false</value> </property> <property> <name>tez.lib.uris</name> <value>/opt/tez/tez.tar.gz</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.execution.engine</name> <value>tez</value> </property> <property> <name>metastore.warehouse.dir</name> <value>/opt/${HIVE_PREFIX}/data/warehouse</value> </property> <property> <name>metastore.metastore.event.db.notification.api.auth</name> <value>false</value> </property> EOF ) cat > /tmp/hive-site-for-metastore.xml << EOF <configuration> ${HIVE_SITE_CONFIG_COMMON} </configuration> EOF cat > /tmp/hive-site-for-hiveserver2.xml << EOF <configuration> <property> <name>hive.metastore.uris</name> <value>thrift://${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME}:9083</value> </property> ${HIVE_SITE_CONFIG_COMMON} </configuration> EOF docker cp ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml /tmp/core-site.xml docker cp ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml /tmp/hdfs-site.xml docker cp ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml /tmp/yarn-site.xml docker cp ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml /tmp/mapred-site.xml cat > /tmp/updated_entrypoint.sh << 'EOF' echo "IS_RESUME=${IS_RESUME} " FLAG_FILE=/opt/hive/already_init_schema if [ -z "${IS_RESUME} " ] || [ "${IS_RESUME} " = "false" ]; then if [ -f ${FLAG_FILE} ]; then echo "Skip init schema when restart." IS_RESUME=true /entrypoint.sh else echo "Try to init schema for the first time." touch ${FLAG_FILE} IS_RESUME=false /entrypoint.sh fi else echo "Skip init schema for every time." IS_RESUME=true /entrypoint.sh fi EOF chmod a+x /tmp/updated_entrypoint.shdocker create --name ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} --network ${SHARED_NS} -p 127.0.0.1:9083:9083 -e SERVICE_NAME=metastore --entrypoint /updated_entrypoint.sh apache/hive:4.0.0 docker cp /tmp/hive-site-for-metastore.xml ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hive/conf/hive-site.xml docker cp /tmp/core-site.xml ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml docker cp /tmp/hdfs-site.xml ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml docker cp /tmp/yarn-site.xml ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml docker cp /tmp/mapred-site.xml ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml docker cp /tmp/updated_entrypoint.sh ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} :/updated_entrypoint.sh docker start ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} docker create --name ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} --network ${SHARED_NS} -p 127.0.0.1:10000:10000 -e SERVICE_NAME=hiveserver2 -e IS_RESUME=true apache/hive:4.0.0 docker cp /tmp/hive-site-for-hiveserver2.xml ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hive/conf/hive-site.xml docker cp /tmp/core-site.xml ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml docker cp /tmp/hdfs-site.xml ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml docker cp /tmp/yarn-site.xml ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml docker cp /tmp/mapred-site.xml ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml docker start ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME}
Test:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 docker exec -it ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} beeline -u 'jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000/' -e " create table hive_example(a string, b int) partitioned by(c int); alter table hive_example add partition(c=1); insert into hive_example partition(c=1) values('a', 1), ('a', 2),('b',3); select * from hive_example; drop table hive_example; "
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 SHARED_NS=hadoop-ns POSTGRES_CONTAINER_NAME=postgres POSTGRES_USER="hive_postgres" POSTGRES_PASSWORD="Abcd1234" POSTGRES_DB="hive-metastore" HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME=hadoop HIVE_PREFIX=hive-with-postgres HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME=${HIVE_PREFIX} -metastore HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME=${HIVE_PREFIX} -server IS_RESUME="false" docker run --name ${POSTGRES_CONTAINER_NAME} --network ${SHARED_NS} \ -e POSTGRES_USER="${POSTGRES_USER} " \ -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD="${POSTGRES_PASSWORD} " \ -e POSTGRES_DB="${POSTGRES_DB} " \ -d postgres:17.0 if [ ! -e /tmp/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin.tar.gz ]; then wget -O /tmp/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin.tar.gz https://downloads.apache.org/tez/0.10.3/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin.tar.gz fi docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c 'mkdir -p /opt/tez' docker cp /tmp/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin.tar.gz ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/tez docker exec ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} bash -c ' if ! hdfs dfs -ls /opt/tez/tez.tar.gz > /dev/null 2>&1; then rm -rf /opt/tez/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin tar -zxf /opt/tez/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin.tar.gz -C /opt/tez hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /opt/tez hdfs dfs -put -f /opt/tez/apache-tez-0.10.3-bin/share/tez.tar.gz /opt/tez fi ' HIVE_SITE_CONFIG_COMMON=$(cat << EOF <property> <name>hive.server2.enable.doAs</name> <value>false</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.tez.exec.inplace.progress</name> <value>false</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.exec.scratchdir</name> <value>/opt/${HIVE_PREFIX}/scratch_dir</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.user.install.directory</name> <value>/opt/${HIVE_PREFIX}/install_dir</value> </property> <property> <name>tez.runtime.optimize.local.fetch</name> <value>true</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.exec.submit.local.task.via.child</name> <value>false</value> </property> <property> <name>mapreduce.framework.name</name> <value>yarn</value> </property> <property> <name>tez.local.mode</name> <value>false</value> </property> <property> <name>tez.lib.uris</name> <value>/opt/tez/tez.tar.gz</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.execution.engine</name> <value>tez</value> </property> <property> <name>metastore.warehouse.dir</name> <value>/opt/${HIVE_PREFIX}/data/warehouse</value> </property> <property> <name>metastore.metastore.event.db.notification.api.auth</name> <value>false</value> </property> EOF ) cat > /tmp/hive-site-for-metastore.xml << EOF <configuration> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL</name> <value>jdbc:postgresql://${POSTGRES_CONTAINER_NAME}/${POSTGRES_DB}</value> </property> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName</name> <value>org.postgresql.Driver</value> </property> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName</name> <value>${POSTGRES_USER}</value> </property> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword</name> <value>${POSTGRES_PASSWORD}</value> </property> ${HIVE_SITE_CONFIG_COMMON} </configuration> EOF cat > /tmp/hive-site-for-hiveserver2.xml << EOF <configuration> <property> <name>hive.metastore.uris</name> <value>thrift://${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME}:9083</value> </property> ${HIVE_SITE_CONFIG_COMMON} </configuration> EOF docker cp ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml /tmp/core-site.xml docker cp ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml /tmp/hdfs-site.xml docker cp ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml /tmp/yarn-site.xml docker cp ${HADOOP_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml /tmp/mapred-site.xml if [ ! -e /tmp/postgresql-42.7.4.jar ]; then wget -O /tmp/postgresql-42.7.4.jar https://jdbc.postgresql.org/download/postgresql-42.7.4.jar fi cat > /tmp/updated_entrypoint.sh << 'EOF' echo "IS_RESUME=${IS_RESUME} " FLAG_FILE=/opt/hive/already_init_schema if [ -z "${IS_RESUME} " ] || [ "${IS_RESUME} " = "false" ]; then if [ -f ${FLAG_FILE} ]; then echo "Skip init schema when restart." IS_RESUME=true /entrypoint.sh else echo "Try to init schema for the first time." touch ${FLAG_FILE} IS_RESUME=false /entrypoint.sh fi else echo "Skip init schema for every time." IS_RESUME=true /entrypoint.sh fi EOF chmod a+x /tmp/updated_entrypoint.shdocker create --name ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} --network ${SHARED_NS} -p 127.0.0.1:9083:9083 -e SERVICE_NAME=metastore -e DB_DRIVER=postgres -e IS_RESUME=${IS_RESUME} --entrypoint /updated_entrypoint.sh apache/hive:4.0.0 docker cp /tmp/hive-site-for-metastore.xml ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hive/conf/hive-site.xml docker cp /tmp/core-site.xml ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml docker cp /tmp/hdfs-site.xml ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml docker cp /tmp/yarn-site.xml ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml docker cp /tmp/mapred-site.xml ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml docker cp /tmp/updated_entrypoint.sh ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} :/updated_entrypoint.sh docker cp /tmp/postgresql-42.7.4.jar ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hive/lib/postgresql-42.7.4.jar docker start ${HIVE_METASTORE_CONTAINER_NAME} docker create --name ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} --network ${SHARED_NS} -p 127.0.0.1:10000:10000 -e SERVICE_NAME=hiveserver2 -e DB_DRIVER=postgres -e IS_RESUME=true apache/hive:4.0.0 docker cp /tmp/hive-site-for-hiveserver2.xml ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hive/conf/hive-site.xml docker cp /tmp/core-site.xml ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml docker cp /tmp/hdfs-site.xml ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml docker cp /tmp/yarn-site.xml ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml docker cp /tmp/mapred-site.xml ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml docker cp /tmp/postgresql-42.7.4.jar ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} :/opt/hive/lib/postgresql-42.7.4.jar docker start ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME}
Test:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 docker exec -it ${HIVE_SERVER_CONTAINER_NAME} beeline -u 'jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000/' -e " create table hive_example(a string, b int) partitioned by(c int); alter table hive_example add partition(c=1); insert into hive_example partition(c=1) values('a', 1), ('a', 2),('b',3); select * from hive_example; drop table hive_example; "
hive_metastore.thrift
1 2 3 4 mkdir hive_metastore_democd hive_metastore_demowget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/hive/master/standalone-metastore/metastore-common/src/main/thrift/hive_metastore.thrift
Modify hive_metastore.thrift, remove fb parts:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 25,26d24 < include "share/fb303/if/fb303.thrift" < 2527c2525 < service ThriftHiveMetastore extends fb303.FacebookService > service ThriftHiveMetastore
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 thrift --gen cpp hive_metastore.thrift mkdir buildgcc -o build/ThriftHiveMetastore.o -c gen-cpp/ThriftHiveMetastore.cpp -O3 -Wall -fPIC gcc -o build/hive_metastore_constants.o -c gen-cpp/hive_metastore_constants.cpp -O3 -Wall -fPIC gcc -o build/hive_metastore_types.o -c gen-cpp/hive_metastore_types.cpp -O3 -Wall -fPIC ar rcs build/libhms.a build/ThriftHiveMetastore.o build/hive_metastore_constants.o build/hive_metastore_types.o cat > main.cpp << 'EOF' using namespace apache::thrift; using namespace apache::thrift::transport; using namespace apache::thrift::protocol; int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { if (argc < 4) { std::cerr << "requires 4 arguments" << std::endl; return 1; } const std ::string hms_ip = argv[1]; const int hms_port = std::atoi(argv[2]); const std::string db_name = argv[3]; const std::string table_name = argv[4]; std::cout << "hms_ip: " << hms_ip << ", hms_port: " << hms_port << ", db_name: " << db_name << ", table_name: " << table_name << std::endl; std::shared_ptr<TTransport> socket(new TSocket(hms_ip , hms_port)); std::shared_ptr<TTransport> transport(new TBufferedTransport(socket)); std::shared_ptr<TProtocol> protocol(new TBinaryProtocol(transport)); Apache::Hadoop::Hive::ThriftHiveMetastoreClient client(protocol); try { transport->open(); // Fetch and print the list of databases std::vector<std::string> databases; client.get_all_databases(databases); std::cout << "Databases:" << std::endl; for (const auto& db : databases) { std ::cout << " " << db << std::endl; } // Fetch and print the list of tables in a specific database std::vector<std::string> tables; client.get_all_tables(tables, db_name); std::cout << "Tables in database '" << db_name << "':" << std::endl; for (const auto& table : tables) { std::cout << " " << table << std::endl; } // Fetch and print the details of a specific table Apache::Hadoop::Hive::Table table; client.get_table(table, db_name, table_name); std::cout << "Table details for '" << table_name << "':" << std::endl; std::cout << " Table name: " << table.tableName << std::endl; std::cout << " Database name: " << table.dbName << std::endl; std::cout << " Owner: " << table.owner << std::endl; std::cout << " Create time: " << table.createTime << std::endl; std::cout << " Location: " << table.sd.location << std::endl; transport->close(); } catch (TException& tx) { std::cerr << "Exception occurred: " << tx.what() << std::endl; } return 0; } EOF gcc -o build/main main.cpp -O3 -Lbuild -lhms -lstdc++ -std=gnu++17 -lthrift -lm build/main <ip> 9083 default hive_test_table
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 CREATE TABLE sales ( sale_id INT , product STRING, amount DOUBLE ) PARTITIONED BY (year INT , month INT ) STORED AS PARQUET; INSERT INTO TABLE sales PARTITION (year = 2023 , month = 6 )VALUES (1 , 'Product A' , 100.0 ), (2 , 'Product B' , 150.0 ), (3 , 'Product C' , 200.0 ); INSERT INTO TABLE sales PARTITION (year = 2023 , month = 7 )VALUES (4 , 'Product D' , 120.0 ), (5 , 'Product E' , 130.0 ), (6 , 'Product F' , 140.0 ); SELECT * FROM sales;
hive.enforce.bucketing: Whether bucketing is enforced. If true, while inserting into the table, bucketing is enforced.
Hive 0.x: false
Hive 1.x: false
Hive 2.x: removed, which effectively makes it always true.
Here’s a example of how to use docker-spark to start a flink cluster and do some tests.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 git clone https://github.com/big-data-europe/docker-flink.git cd docker-flinkdocker-compose up -d cat > person.csv << 'EOF' 1,"Tom" ,18 2,"Jerry" ,19 3,"Spike" ,20 4,"Tyke" ,21 EOF docker exec flink-master mkdir -p /opt/data docker exec flink-worker mkdir -p /opt/data docker cp person.csv flink-master:/opt/data/person.csv docker cp person.csv flink-worker:/opt/data/person.csv docker exec -it flink-master bash sql-client.sh CREATE TABLE person ( id INT, name STRING, age INT ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'filesystem' , 'path' = 'file:///opt/data/person.csv' , 'format' = 'csv' ); SELECT * FROM person;