阅读更多
1 Basic Concept
1.1 Mode
Three commonly used modes in Vim: Normal mode, Insert mode, and Command-line mode. Use :help mode for more details.
Normal mode, Insert mode, and Command-line mode can switch between each other, but Insert mode and Command-line mode cannot switch directly between each other.
1.1.1 Normal Mode
When you open a file with Vim, it starts in Normal mode (this is the default mode).
In this mode, you can use the arrow keys to move the cursor, delete characters or entire lines, and copy and paste content in your file.
1.1.2 Insert Mode
In Normal mode, you can perform operations like delete, copy, and paste, but you cannot edit the file content. You must press one of the keys like i(I), o(O), a(A), or r(R) to enter Insert mode.
To return to Normal mode, simply press the Esc key to exit the editor mode.
1.1.3 Visual Mode
This mode is used for selecting and manipulating text visually.
1.1.4 Command-line Mode
In Normal mode, pressing any of the keys :, /, or ? will move the cursor to the bottom line. This enters Command-line mode, where you can perform search operations.
Actions like reading and saving files, bulk character replacement, exiting Vim, displaying line numbers, and more are also carried out in this mode.
1.1.5 Ex Mode
This is an even more powerful mode than command-line mode, used for advanced editing and automation.
Ex mode, on the other hand, is a more powerful command-line mode that is entered by typing Q or q: from normal mode or insert mode
1.2 Buffer
Each opened file corresponds to a buffer. A buffer can be visible or hidden.
1.3 Window
A window is the interface we see and interact with. A window can contain one or more buffers, but it always displays one buffer (a file or an empty one). Multiple windows can be opened simultaneously.
1.4 Tab
A tab can contain one or more windows. If multiple tabs exist, they will be displayed at the top, similar to a modern editor like VSCode.
2 Operation Manual
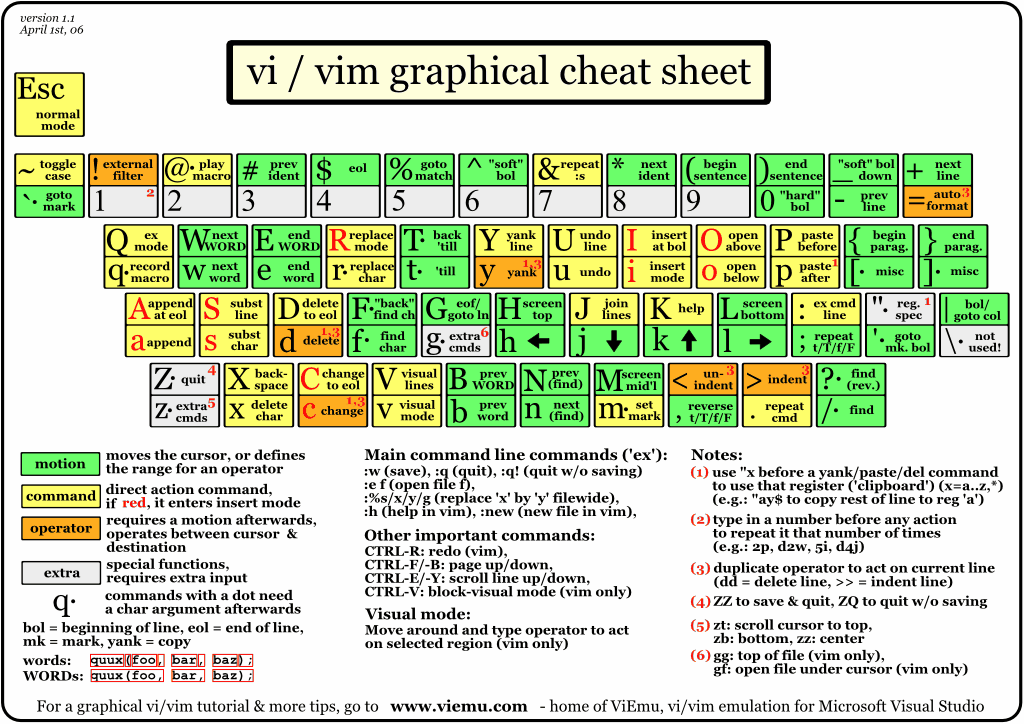
2.1 Insert Mode
i,I: Enter Insert mode;iinserts at the cursor position,Iinserts at the first non-blank character of the current line.a,A: Enter Insert mode;ainserts after the cursor position,Ainserts at the end of the current line.o,O: Enter Insert mode;oopens a new line below the current line,Oopens a new line above the current line.s,S: Enter Insert mode;sdeletes the character under the cursor,Sdeletes the entire current line.r,R: Enter Replace mode;rreplaces the single character under the cursor once,Rcontinuously replaces characters on the current line untilEscis pressed.Esc: Return to Normal mode.[Ctrl] + [(:help i_CTRL-[): Return to Normal mode.[Ctrl] + w(:help i_CTRL-W): Delete the previous word.[Ctrl] + r + [reg]: Insert content from a register, for example:[Ctrl] + r + 0: Insert content from register0.[Ctrl] + r + ": Insert content from the default register.
[Ctrl] + r + =: Insert the result of an expression; expression follows the equal sign.[Ctrl] + r + /: Insert the last searched keyword.[Ctrl] + o + [cmd]: Temporarily exit Insert mode to execute a single command, then return to Insert mode.[Ctrl] + o + 0: Move cursor to the beginning of the line, equivalent to0in Normal mode.
[Ctrl] + d/t/f: Decrease/Increase/Adjust indentation of the current line.[Shift] + [Left]: Move cursor left by one word.[Shift] + [Right]: Move cursor right by one word.[Shift] + [Up]: Page up.[Shift] + [Down]: Page down.[Ctrl] + e(:help i_CTRL-E): Insert the character which is below the cursor.[Ctrl] + y(:help i_CTRL-Y): Insert the character which is above the cursor.
2.2 Moving Cursor
Character-wise Movement:
j/[n]j: Move down by 1/n line.k/[n]k: Move up by 1/n line.h/[n]h: Move left by 1/n character.l/[n]l: Move right by 1/n character.f<x>/[n]f<x>: Move to the next 1/n occurrence of<x>in the current line.F<x>/[n]F<x>: Move to the previous 1/n occurrence of<x>in the current line.t<x>/[n]t<x>: Move to just before the next 1/n occurrence of<x>in the current line.T<x>/[n]T<x>: Move to just after the previous next 1/n occurrence of<x>in the current line.;: Repeat the lastf/F/t/Tcommand.,: Repeat the lastf/F/t/Tcommand in the opposite direction.
[n][space]: Move right by n character.0: Move to the beginning of the line.^: Move to the first non-blank character of the line.$: Move to the end of the line.g_: Move to the last non-blank character of the line.gm: Move to the middle character of the line.
Word-wise Movement:
w: Move to the start of the next word.W: Move to the start of the next word (words are delimited by spaces).e: Move to the end of the next word.E: Move to the end of the next word (words are delimited by spaces).b: Move to the beginning of the previous word.B: Move to the beginning of the previous word (words are delimited by spaces).ge: Move to the end of the previous word.gE: Move to the end of the previous word (words are delimited by spaces).
Line-wise Movement:
gj: Move down by one visual line (It works with wrapped lines).gk: Move up by one visual line (It works with wrapped lines).+: Move to the first non-blank character of the next line.-: Move to the first non-blank character of the previous line.G: Move to the last line of the file.[n]G: Move to a specific line<n>.gg: Move to the first line of the file.[n][Enter]: Move to the next n lines.H: Move to the top of the screen.M: Move to the middle of the screen.L: Move to the bottom of the screen.
Screen-wise Movement:
<c-f>: Move forward by one full screen.<c-b>: Move backward by one full screen.<c-d>: Move down by half a screen.<c-u>: Move up by half a screen.<c-e>: Scroll the screen down by one line.<c-y>: Scroll the screen up by one line.zz: Put the current line in the middle of the screen.zt: Put the current line in the top of the screen.zb: Put the current line in the bottom of the screen.
Paragraph and Section Movement:
): Move to next sentence.(: Move to previous sentence.}: Move to next paragraph.{: Move to previous paragraph.]): Move to next unmatched).[(: Move to previous unmatched(.]}: Move to next unmatched}.[{: Move to previous unmatched{.]m: Move to next start of a method.[m: Move to previous start of a method.]M: Move to next end of a method.[M: Move to previous end of a method.%: Move to matched of{} () [].- You can add recognition for angle brackets
<>by using:set matchpairs+=<:>. It may cause misrecognition, as the text may contain single>or<.
- You can add recognition for angle brackets
=: Adjust indent.gg=G
2.2.1 Jump List
Help documentation: :help jump-motions
Commands that move the cursor across multiple lines are called jump commands, for example:
H,M,L123G,:123: Jump to the specified line/[word],?[word],:s,n,N: Search and replace%,(),[],{}'': Return to the last position in the jump list; the cursor loses column info and is placed at the start of the line. This command itself is also a jump and will be recorded in the jump list.~~: Return to the last position in the jump list; the cursor will be positioned exactly at the previous column. This command is also a jump and will be recorded in the jump list.[Ctrl] + o: Return to the previous position in the jump list; this command itself is not a jump and will not be recorded in the jump list.[Ctrl] + i: Return to the next position in the jump list; this command itself is not a jump and will not be recorded in the jump list.:jumps: Display the jump list:clearjumps: Clear the jump list
2.2.2 Change List
Help documentation: :help changelist
When content is modified, the location of the change is recorded. You can navigate between these recorded positions in the change list using the following commands:
g;: Jump to the previous position in the change listg,: Jump to the next position in the change list:changes: Display the change list
2.2.3 Mark
m<letter>: Set a mark. Lowercase for local mark, uppercase for global mark.'<letter>: Jump to a mark.
2.3 Text Editing
Commands like c, d, etc., can be combined with cursor movement commands:
dd: Delete the entire line where the cursor is located.dw: Delete from the cursor to the end of the current word.[n]dd: Delete the current line and the nextn-1lines (including the current line).d1G: Delete from the current line up to line 1 (including the current line).dG: Delete from the current line to the last line (including the current line).d0(zero): Delete from the cursor position to the beginning of the line (excluding the character under the cursor).d^: Delete from the cursor position to the first non-blank character of the line (excluding the character under the cursor).d$: Delete from the cursor position to the end of the line (including the character under the cursor).d%: Delete from the character under the cursor (which must be on a bracket —(,[, or{) to its matching closing bracket, including all characters in between.df<x>/d[n]f<x>: Delete from the cursor position up to and including the first/nth occurrence of characterx.dt<x>/d[n]t<x>: Delete from the cursor position up to (but not including) the first/nth occurrence of characterx.d/<word>: Delete from the cursor position up to (but not including) the next occurrence of the search keyword<word>.D: Same asd$.cc: Change (replace) the entire current line.cw: Change from the cursor position to the end of the current word.[n]cc: Change the current line and the nextn-1lines.c1G: Change from the current line up to line 1.cG: Change from the current line to the last line.c0(zero): Change from the cursor to the beginning of the line (excluding the cursor character).c^: Change from the cursor to the first non-blank character of the line (excluding the cursor character).c$: Change from the cursor to the end of the line (including the cursor character).c%: Change from the character under the cursor (must be a bracket —(,[,{) to its matching closing bracket.cf<x>/c[n]f<x>: Change from the cursor up to and including the first/nth occurrence of characterx.ct<x>/c[n]t<x>: Change from the cursor up to (but not including) the first/nth occurrence of characterx.c/<word>: Change from the cursor up to (but not including) the next occurrence of the search keyword<word>.- Use
n/Nto find the next/previous match; press.to repeat the last change.
- Use
C: Same asc$.
Others:
J: Join the current line with the next line.x,X: Delete one character;xdeletes forward (like[Del]),Xdeletes backward (like[Backspace]).[n]x: Deletencharacters forward.g~/gu/gU: Toggle case/convert to lowercase/convert to uppercase; usually combined with a text object, for example:guiwguw
<: Decrease indentation.>: Increase indentation.[Ctrl] + a: Increment number under cursor by 1.[Ctrl] + x: Decrement number under cursor by 1.u: Undo the last operation.[Ctrl] + r: Redo the last undone operation..: Repeat the last operation.
2.4 Copy & Paste
yy: Yank (copy) the entire line where the cursor is located.[n]yy: Yank the current line and the nextn-1lines (including the current line).y1G: Yank from the current line up to line 1 (including the current line).yG: Yank from the current line to the last line (including the current line).y0(zero): Yank from the cursor position to the beginning of the line (excluding the character under the cursor).y$: Yank from the cursor position to the end of the line (including the character under the cursor).p: Paste the yanked text after the cursor.P: Paste the yanked text before the cursor.
2.4.1 Register
Vim has many registers (these are not CPU registers), including:
0-9: Vim uses these to store recent copy, delete, and other operations0: Stores the most recent copy (yank) content1-9: Store the most recent deletes; the latest delete goes into1. When a new delete happens, the oldiregister content moves toi+1. Since9is the max, content in register9is discarded.
a-zA-Z: User registers; Vim does not read or write these automatically": The unnamed register. All delete and copy operations default to this anonymous register.*: System clipboard register- On
Mac/Windows: Same as+ - On
Linux-X11: Represents the selected mouse region; middle-click pastes on desktop environments
- On
+: System clipboard register- On
Mac/Windows: Same as* - On
Linux-X11: On desktop, can paste withCtrl+V
- On
_: The “black hole register”, similar to/dev/nullin file systems (discard register)
How to use these registers: "<reg name><operator>
- The leading
"is fixed syntax <reg name>: Register name, e.g.,0,a,+,"etc.<operator>: Operation to perform, likey(yank),d(delete),p(paste), etc.q<reg name>q: Clear the content of a register
Examples:
:reg: Show information about all registers:reg <reg name>: Show the content of a specific register"+yy: Yank the current line into the system clipboard register"+p: Paste content from the system clipboard register after the cursor
How to paste the local system clipboard content into Vim on a remote host via SSH?
- First, confirm if Vim on the remote host supports
clipboardby runningvim --version | grep clipboard.-clipboardmeans no support;+clipboardmeans supported. Clipboard support requires an X environment. - If the system is CentOS, install a graphical environment like
GNOME, then installvim-X11, and usevimxinstead ofvim. Runningvimx --version | grep clipboardshould show clipboard support. Then you can usevimxin the SSH terminal to access the remote clipboard. - To be continued — sharing the clipboard between local and remote machines is not yet solved.
2.5 Visual Selection
v: Character-wise visual selection; highlights characters as the cursor moves.vw: Select from the cursor position to the end of the current word (if cursor is inside a word, it won’t select the entire word).viw: Select the entire word under the cursor (even if the cursor is in the middle of the word).vi': Select content inside single quotes.vi": Select content inside double quotes.vi(: Select content inside parentheses.vi[: Select content inside square brackets.vi{: Select content inside curly braces.V: Line-wise visual selection; highlights entire lines as the cursor moves.<line number>G: Jump to the specified line and visually select all lines in between.
[Ctrl] + v: Block-wise visual selection; allows rectangular selection of text.>: Increase indentation.<: Decrease indentation.~: Toggle case.c/y/d: Change/Yank (copy)/Delete.u: Change to lowercase.U: Change to uppercase.o: Jump to the other end of the visual selection.O: Jump to the other end of the visual block.gv: After usingporPto replace a selection, reselect the replaced area.gn: Select the next search match.gN: Select the previous search match.
2.6 Search & Replace
- Search
/[word]: Search downward for a string namedword, supports regular expressions./\<[word]\>: Search downward for the exact whole wordword(word boundary match), supports regular expressions./\V[word]: Search downward for the literal stringwordwhere all characters (except/) are treated as normal characters.?[word]: Search upward for a string namedword, supports regular expressions.?\<[word]\>: Search upward for the exact whole wordword, supports regular expressions.?\V[word]: Search upward for the literal stringwordwhere all characters (except?) are treated as normal characters.n: Repeat the previous search in the same direction.N: Repeat the previous search in the opposite direction.*: Search forward for the keyword under the cursor in whole word mode (\<[word]\>). The keyword selection rules:- Keyword under the cursor
- The nearest keyword after the cursor on the current line
- Non-blank string under the cursor
- The nearest non-blank string after the cursor on the current line
- Case sensitivity:
/[word]\c: Case insensitive search./[word]\C: Case sensitive search.
#: Like*, but searches backward.g*: Like*, but searches for partial matches (non-whole word).g#: Like#, but searches for partial matches.- To search the last visually selected text, follow these steps:
- Enter visual mode
- Yank with
y - Enter search mode with
/ - Insert register content with
[Ctrl] + r - Enter default register with
"
- Replace
:[n1],[n2]s/[word1]/[word2]/g: Search forword1between linesn1andn2and replace withword2, supports regular expressions.:[n1],[n2]s/\<[word1]\>/[word2]/g: Same as above but with whole word matching.:1,$s/[word1]/[word2]/gor:%s/[word1]/[word2]/g: Search and replaceword1withword2from the first to the last line, supports regular expressions.:1,$s/[word1]/[word2]/gcor:%s/[word1]/[word2]/gc: Same as above but prompts for confirmation before each replacement.- In visual mode, select a range and enter
:s/[word1]/[word2]/gcto replace within the selection.
[Ctrl]+rand[Ctrl]+w: Add the string under the cursor to the search or replace expression.gn: Select the next search match.gN: Select the previous search match.
2.7 Record
Record refers to a feature that allows you to record a sequence of keystrokes and save it as a macro for later playback. This is a powerful and versatile feature that can help you automate repetitive tasks, make complex edits more efficiently, and improve your overall productivity when working with text.
How to Use Vim Record:
- Start Recording: To start recording a macro, press
qfollowed by the register(atoz) where you want to store the macro. For example, press qa to start recording in registera - Perform Actions: While recording is active, perform the series of commands, edits, or movements you want to include in your macro. Vim will record everything you do.
- Stop Recording: To stop recording, press
qagain. In our example, pressqonce more to stop recording in registera - Replay the Macro: To replay the recorded macro, use the
@symbol followed by the register where you stored the macro. For example, to replay thearegister macro, type@a
2.8 File
:w: Save the current file.:wa: Save all files.:w!: Force write to the file if it is read-only; whether it succeeds depends on your file system permissions.:q: Quit Vim.:q!: Quit without saving changes (force quit).:wq: Save and quit;:wq!forces save and quit.:e [filename]: Open and edit the specified file.:e: Reload the current file.ZZ: If the file is unchanged, quit without saving; if changed, save and quit.:w [filename]: Save the current buffer to a different file (note the space betweenwand filename).:r [filename]: Read the content of another file and insert it after the cursor line (note the space betweenrand filename).:[n1],[n2]w [filename]: Write linesn1ton2to the specified file (space betweenwand filename; space between[n2]andwoptional).vim [filename1] [filename2]...: Edit multiple files simultaneously.:n: Edit the next file.:N: Edit the previous file.:files: List all files opened by this Vim session.:file: Show the current file’s path.:Vex: Open the directory explorer.
2.9 Text Object
Text objects: Commands like c, d, v, y, g~, gu, gU are followed by text objects, generally in the format: <scope><type>
- Scope: Optional values are
aandia: Includes the boundariesi: Excludes the boundaries
- Type: Parentheses, braces, brackets, single quotes, double quotes, etc.
'"(/b[{/B
Examples:
i): Inside parentheses (excluding the parentheses themselves)a): Inside parentheses (including the parentheses)i]: Inside square brackets (excluding the brackets)a]: Inside square brackets (including the brackets)i}: Inside curly braces (excluding the braces)a}: Inside curly braces (including the braces)i': Inside single quotes (excluding the quotes)a': Inside single quotes (including the quotes)i": Inside double quotes (excluding the quotes)a": Inside double quotes (including the quotes)
2.10 Text Fold
According to the folding rules, there are 4 types:
manual(manual folding):set foldmethod=manualzf: Create a fold, used with a motion or visual rangezfcan also be combined with text objects, for example:zfi{: Fold the content inside curly braces, excluding the lines with the braces themselveszfa{: Fold the content inside curly braces, including the lines with the braces
zd/zD: Delete the current foldzE: Delete all folds
indent(indentation-based folding):set foldmethod=indent:set foldlevel=[n]
marker(marker folding):set foldmethod=marker
syntax(syntax-based folding):set foldmethod=syntax
Common operations (uppercase commands are recursive):
zN: Enable foldingzn: Disable foldingza/zA: Toggle fold (fold/unfold) on the current code blockzc/zC: Close (fold) the current foldzo/zO: Open (unfold) the current foldzm/zM: Fold all foldszr/zR: Open all foldszj: Move to the next foldzk: Move to the previous fold
2.11 Buffer
:buffers: List all buffers.:buffer [n]: Switch to the specified buffer.:bnext: Switch to the next buffer.:bprev: Switch to the previous buffer.:edit [filename]: Load a file into a new buffer.:bdelete [n]: Delete the specified buffer (if no number given, deletes the current buffer).:%bdelete: Delete all buffers.:%bdelete|e#: Delete all buffers except the current one;:e#reopens the last closed buffer.
:bufdo <cmd>: Execute a command on all buffers.:bufdo e: Reload the files corresponding to all buffers.
2.12 Window
[Ctrl] + w + <xxx>: Press[Ctrl]thenw, release both, then press<xxx>. The following operations are based on this sequence.vim -On file1 file2...: Vertical split windows.vim -on file1 file2...: Horizontal split windows.[Ctrl] + w + c: Close the current window (cannot close the last one).[Ctrl] + w + q: Close the current window (can close the last one).[Ctrl] + w + o: Close all other windows except the current one.[Ctrl] + w + s: Split the current file horizontally.[Ctrl] + w + v: Split the current file vertically.:sp filename: Split horizontally and open a new file.:vsp filename: Split vertically and open a new file.[Ctrl] + w + l: Move the cursor to the window on the right.[Ctrl] + w + h: Move the cursor to the window on the left.[Ctrl] + w + k: Move the cursor to the window above.[Ctrl] + w + j: Move the cursor to the window below.[Ctrl] + w + w: Move the cursor to the next window (toggles between two windows if only two).[Ctrl] + w + L: Move the current window to the far right.[Ctrl] + w + H: Move the current window to the far left.[Ctrl] + w + K: Move the current window to the top.[Ctrl] + w + J: Move the current window to the bottom.[Ctrl] + w + =: Make all windows equal height and width.[Ctrl] + w + [+]: Increase window height by 1.[Ctrl] + w + [n] + [+]: Increase window height by n.[Ctrl] + w + -: Decrease window height by 1.[Ctrl] + w + [n] + -: Decrease window height by n.[Ctrl] + w + >: Increase window width by 1.[Ctrl] + w + [n] + >: Increase window width by n.[Ctrl] + w + <: Decrease window width by 1.[Ctrl] + w + [n] + <: Decrease window width by n.
2.13 Tab
:tabnew [filename]: Open a file in a new tab.:tabnew %: Open the current file in another tab.
:tabedit: Same astabnew.:tabm [n]: Move the current tab to positionn(starting from 0). Ifnis not specified, move to the last position.gt/:tabnext: Go to the next tab.gT/:tabprev: Go to the previous tab.:tab sball: Open all buffers in tabs.:tabdo <cmd>: Execute a command on all tabs.:tabdo e: Reload the files corresponding to all tabs.
2.14 Quickfix
:copen: Open the quickfix window (view compile, grep, etc. information).:copen 10: Open the quickfix window with a height of 10.:cclose: Close the quickfix window.:cfirst: Jump to the first error in quickfix.:clast: Jump to the last error in quickfix.:cc [nr]: View error number[nr].:cnext: Jump to the next error in quickfix.:cprev: Jump to the previous error in quickfix.:set modifiable: Make quickfix writable, allowing deletion of entries using commands likedd.
2.15 Terminal
Vim can embed a terminal
:terminal: Open the terminal.[Ctrl] + \ + [Ctrl] + n: Exit terminal mode.
2.16 Mapping
map: Recursive mappingnoremap: Non-recursive mappingunmap: Reset specified key to default behaviormapclear: Clear allmapconfigurations, use with caution
| COMMANDS | MODES |
|---|---|
map、noremap、unmap |
Normal, Visual, Select, Operator-pending |
nmap、nnoremap、nunmap |
Normal |
vmap、vnoremap、vunmap |
Visual and Select |
smap、snoremap、sunmap |
Select |
xmap、xnoremap、xunmap |
Visual |
omap、onoremap、ounmap |
Operator-pending |
map!、noremap!、unmap! |
Insert and Command-line |
imap、inoremap、iunmap |
Insert |
lmap、lnoremap、lunmap |
Insert, Command-line, Lang-Arg |
cmap、cnoremap、cunmap |
Command-line |
tmap、tnoremap、tunmap |
Terminal-Job |
View all map commands:
:map:map <c-l>:map <f5>:map \rn
:noremap:nnoremap
Redirect all map commands to a file:
:redir! > vim_keys.txt:silent verbose map:redir END
Special parameters:
<buffer>: The mapping applies only to the current buffer.<nowait><silent>: Disable showing mapping messages.<special><script><expr><unique>
2.17 Key Representation
<f-num>: For example,<f1>,<f2>.<c-key>: Represents[Ctrl]plus another key.<a-key>/<m-key>: Represents[Alt]plus another key.- On Mac, there is no
<p-key>for[Option]. Instead, the actual output character produced by pressing[Option]plus another key is used as the mapping key, for example:[Option] + a:å
2.18 Config
:set <config>?: View the value of<config>.verbose set <config>?: Shows the source of the configuration.:set filetype?: View the file type.
:echo &<config>: Also view the value of<config>.:echo &filetype: View the file type.
set <config> += <value>: Add to a setting; multiple items can be added separated by commas.set <config> -= <value>: Remove from a setting; only one item can be removed at a time.
2.18.1 Frequently-used Configs
1 | :set nocompatible " Set to be incompatible with original vi mode (must be set at the very beginning) |
2.18.2 Debugging Configs
runtimepath(rtp): Specifies the directory paths Vim will use to search for runtime files.path: Sets the list of directories to be searched when using commands like :find.packpath: Determines where Vim looks for packages.backupdir(bdir): Specifies the directory for backup files.directory(dir): Indicates where swap files are stored.spellfile: Defines the file locations for spell checking.undodir: Designates the directory for undo files.viewdir: Specifies the directory for saved views.backupskip: Lists patterns for files that should not have backups.wildignore: Sets the patterns to be ignored during file name completion.suffixes: Defines suffixes that are less important during filename matching.helpfile: Specifies the location of the help file.tags: Lists the tag files used for tag commands.
2.18.3 Config File
Vim actively records your past actions so that you can easily continue your work next time. The file that stores these records is ~/.viminfo.
Global Vim settings are generally placed in /etc/vimrc (or /etc/vim/vimrc). It is not recommended to modify this file directly. Instead, you can modify your personal configuration file ~/.vimrc (which does not exist by default and must be created manually).
When running Vim, if you modify the contents of ~/.vimrc, you can reload it immediately by executing :source ~/.vimrc or :so % to apply the new configurations.
2.19 Variable
Neovim supports several types of variables:
- Global Variables
(g:): These are accessible from anywhere in your Neovim configuration and during your Neovim sessions. They are often used to configure plugins and Neovim settings. - Buffer Variables
(b:): These are specific to the current buffer (file) you are working on. Changing the buffer will change the scope and access to these variables. - Window Variables
(w:): These are specific to the current window. Neovim allows multiple windows to be open, each can have its own set of w: variables. - Tab Variables
(t:): These are associated with a specific tab in your Neovim environment. - Vim Variables
(v:): These are built-in variables provided by Neovim that contain information about the environment, such as v:version for the Neovim version or v:count for the last used count for a command.
Setting Variables:
1 | let g:my_variable = "Hello, Neovim!" |
Accessing Variables:
1 | :echo g:my_variable |
Unsetting Variables:
1 | :unlet g:my_variable |
2.20 Help Doc
:help CTRL-W: View help forctrl + win normal mode.:help i_CTRL-V: View help forctrl + vin insert mode (i_means insert mode).:help v_CTRL-A: View help forctrl + ain visual mode (v_means visual mode).:help :s: View help for the:scommand.
Documentation path: /usr/share/vim/vim82/doc
/usr/share/vim/vim82/doc/help.txt: Main documentation file.
vimtutor: Provides a simple tutorial.
2.21 Troubleshooting
vim -V10logfile.txtecho &runtimepath
2.22 Assorted
echo:echom xxx: The message will be saved in the message history, which can be viewed with:message.
- Command history
q:: Enter command-line history editing.q/: Enter search history editing.- **
q[a-z]**: Pressq` followed by any letter to enter command history. - You can edit a command like editing a buffer, then press Enter to execute it.
- Press
[Ctrl] + cto exit history editing and return to the editing buffer; however, the history editing window remains open, allowing you to refer to previous commands and input your own. - Type
:xto close history editing and discard changes, returning to the editing buffer. - Pressing Enter on an empty command also exits history editing and returns to the editing buffer.
[Ctrl] + g: Show file statistics.g + [Ctrl] + g: Show byte statistics.
2.22.1 Symbol Index
[Ctrl] + ]: Jump to the definition of the symbol under the cursor.gf: Jump to the header file under the cursor.- Use
set path=orset path+=to set or add header file search paths. - Use
set path?to view the current value of this variable.
- Use
[Ctrl] + ^: Switch between the two most recently edited files.
2.22.2 Insert Form Feed(tab)
Referring to How can I insert a real tab character in Vim?, after setting parameters like tabstop, softtabstop, and expandtab, the tab key will be replaced by spaces. If you want to insert a literal \t character, you can press [Ctrl] + v + i in insert mode, where:
[Ctrl] + vmeans to input the literal character.irepresents the\tcharacter.
2.22.3 Multiply-line Editing
Example: Insert the same content on multiple lines simultaneously
- At the column where you need to insert content, press
[Ctrl] + vand select the lines to modify simultaneously - Press
Ito enter insert mode - Type the text you want to insert
- Press
esctwice
Example: Insert the same content at the end of multiple lines simultaneously
- At the column where you need to insert content, press
[Ctrl] + vand select the lines to modify simultaneously - Press
$to move to the end of the line - Press
Ato enter insert mode - Type the text you want to insert
- Press
esctwice
Example: Delete the same content on multiple lines simultaneously
- At the column where you need to delete content, press
[Ctrl] + vand select the lines to modify simultaneously - Select the columns to delete simultaneously
- Press
dto delete simultaneously
2.22.4 Chinese Garbled Text
Edit /etc/vimrc and append the following content
1 | set fileencodings=utf-8,ucs-bom,gb18030,gbk,gb2312,cp936 |
2.22.5 Project Customized Config
The same ~/.vimrc cannot be used for all projects. Different projects may require some specialized configuration options. You can use the following setup method.
1 | if filereadable("./.workspace.vim") |
3 Plugin
3.1 Overview
3.1.1 Plugin Manager
3.1.1.1 vim-plug
Home: vim-plug
Install:
1 | curl -fLo ~/.vim/autoload/plug.vim --create-dirs \ |
Usage:
-
Config
1
2
3
4
5
6call plug#begin()
" List your plugins here
Plug 'tpope/vim-sensible'
call plug#end() -
:PlugStatus -
:PlugInstall -
:PlugClean
Update source(~/.vim/autoload/plug.vim):
1 | " Change |
How to install plugins from different sources:
- Option 1: Specify the full URL of the plugin. For example, change
Plug 'morhetz/gruvbox'toPlug 'https://github.com/morhetz/gruvbox'. - Option 2: Disable
URIvalidation. By default,Plugdoes not allow plugins from different sources. To disable this feature, modify~/.vim/autoload/plug.vimas follows:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10" Delete following code snippet
elsif !compare_git_uri(current_uri, uri)
[false, ["Invalid URI: #{current_uri}",
"Expected: #{uri}",
"PlugClean required."].join($/)]
" Delete following code snippet
elseif !s:compare_git_uri(remote, a:spec.uri)
let err = join(['Invalid URI: '.remote,
\ 'Expected: '.a:spec.uri,
\ 'PlugClean required.'], "\n")
3.1.1.1.1 Tips
echo g:plug_home: show home dir.
3.1.1.2 packer.nvim
Home: packer.nvim
Install:
1 | git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/wbthomason/packer.nvim\ |
Configuration:
-
~/.config/nvim/init.vim1
2
3if has('nvim')
lua require('packer-plugins')
endif -
~/.config/nvim/lua/packer-plugins.lua1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8vim.cmd [[packadd packer.nvim]]
return require('packer').startup(function(use)
-- Packer can manage itself
use 'wbthomason/packer.nvim'
-- Your plugins
end)
Usage:
PackerCompile: You must run this orPackerSyncwhenever you make changes to your plugin configuration. Regenerate compiled loader file.PackerClean: Remove any disabled or unused plugins.PackerInstall: Clean, then install missing plugins.PackerStatus: Show list of installed plugins.
3.2 Prepare
**Why is it necessary to prepare the environment? Doesn’t vim’s plugin manager install plugins for us?**Because certain complex plugins, such as ycm, require manual compilation, and the compilation process depends on some build-related tools, often with relatively high version requirements.
Since the system I’m using is CentOS 7.9, the tools installed via yum install are too outdated, including gcc, g++, clang, clang++, cmake, etc. These tools all need to be reinstalled through other means.
3.2.1 vim8 (Required)
Many of the plugins mentioned above have version requirements for vim, requiring at least vim8. However, the version of vim installed via yum install is generally 7.x.
1 | # Uninstall |
3.2.2 Symbol-ctags (Recommend)
Home: ctags
The full name of ctags is universal-ctags
Installation: Refer to the official GitHub documentation for compilation and installation
1 | git clone https://github.com/universal-ctags/ctags.git --depth 1 |
ctags parameters:
--c++-kinds=+px:ctagsrecords function declarations in C++ files, including various external and forward declarations.--fields=+ailnSz: Specifies the information thatctagsshould describe, where:a: If the element is a class member, mark its access level (i.e., public or private).i: If there is inheritance, indicate the parent class.l: Mark the language of the source file containing the tag.n: Mark the line number.S: Mark the function signature (i.e., function prototype or parameter list).z: Mark thekind.
--extras=+q: Forcesctagsto perform the following — if a syntax element is a class member,ctagswill normally record one line for it. This option instructsctagsto record another line for the same syntax element to ensure that in VIM, multiple functions with the same name can be distinguished by different paths.-R:ctagsrecursively generates tags for subdirectories (very useful when executed in the root directory of a project).
Generate ctags in a project:
1 | # To match the configuration in the above ~/.vimrc, the tag file name needs to be specified as .tags |
How to generate ctags for the C/C++ standard library — the resulting ctags file for the standard library will be located at ~/.vim/.cfamily_systags
1 | mkdir -p ~/.vim |
How to generate ctags for the Python standard library — the resulting ctags file for the standard library is~/.vim/.python_systags(ctags, vim and python code)
1 | ctags --languages=python --python-kinds=-iv --fields=+ailnSz --extras=+q -R -f ~/.vim/.python_systags /usr/lib64/python3.6 |
Usage:
[Ctrl] + ]: Jump to the definition of the symbol. If there are multiple matches, it jumps to the first one.[Ctrl] + w + ]: Jump to the symbol definition in a new window. If there are multiple matches, it jumps to the first one.:ts: Show all matching items. PressESC, then enter the number, and pressEnterto jump to the specified match.:tn: Jump to the next matching item.:tp: Jump to the previous matching item.g + ]: If there are multiple matches, it directly displays them (same as:ts).
Configuration (~/.vimrc):
- Note that the tag file name has been changed from
tagsto.tagsto avoid polluting other files in the project. Therefore, when generating the tag file with thectagscommand, you need to specify the file name with the-f .tagsparameter. ./.tags;means searching for the.tagssymbol file in the directory of the current file. The;means that if it is not found, the search recurses upwards to the parent directories until.tagsor the root directory is found..tagsrefers to searching for the.tagsfile in the current directory of vim (check with:pwdinside vim).
1 | " tags search mode |
3.2.3 Symbol-cscope (Optional)
Home: cscope
Compared to ctags, cscope supports more features, including finding definitions, finding references, and more. However, the project was last updated in 2012, so it is not recommended to use. Instead, gtags is recommended.
Install:
1 | wget -O cscope-15.9.tar.gz 'https://sourceforge.net/projects/cscope/files/latest/download' --no-check-certificate |
How to use the command-line tools:
1 | # Create an index — this command generates an index file named cscope.out in the current directory |
How to use it in vim
1 | " Add database |
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | " Enable quickfix |
Notes:
- Try to create the database in the source code directory; otherwise, cscope will scan all files by default, which is very inefficient.
3.2.4 Symbol-gtags (Optional)
Home: gtags
The full name of gtags is GNU Global source code tagging system
Here is a pitfall: the gcc-10.3.0 installed above will cause an error when compiling and installing the global source code (see dev-util/global-6.6.4 : fails to build with -fno-common or gcc-10). The error message is roughly global.o:(.bss+0x74): first defined here. Therefore, we need to install a lower version of gcc and use that lower version of gcc to compile global.
1 | # Install repo |
1 | # Install dependencies |
How to use the command-line tools:
1 | # Treat header files as source files for parsing; otherwise, symbols in header files may not be recognized |
Configuration (~/.vimrc):
- The first
GTAGSLABELtellsgtagsto use the local analyzer for six natively supported languages such asC/C++/Java, while other languages use thepygmentsmodule. - The second environment variable must be set (in my environment, it works without setting it), otherwise
native-pygmentsand thelanguage mapdefinitions will not be found.
1 | " Setting native-pygments causes "gutentags: gtags-cscope job failed, returned: 1", so I changed it to native |
**FAQ: **
global -dcannot find class definitions; possible reasons include:- Classes marked with
final—gtagscannot find their definitions, a frustrating bug that caused me a lot of trouble.
- Classes marked with
global -dcannot find definitions of member variables.
3.2.5 LSP-clangd (Recommend)
clangd is an implementation of LSP (Language Server Protocol), mainly used for languages such as C/C++/Objective-C.
3.2.6 LSP-ccls (Optional)
ccls is an implementation of LSP (Language Server Protocol), mainly used for languages such as C/C++/Objective-C.
Installation: Refer to the official GitHub documentation for compilation and installation
1 | git clone https://mirror.ghproxy.com/https://github.com/MaskRay/ccls.git |
How to generate a full index for the project?
- Use build tools like
cmaketo generatecompile_commands.jsonand place this file in the root directory of the project. - Configure the
LSP-clientplugin; I useLanguageClient-neovim. - Open the project in vim, and the index will be created automatically.
3.2.7 LSP-jdtls (Optional)
jdtls is an implementation of LSP (Language Server Protocol), mainly used for the Java language
Installation: Refer to the official GitHub documentation for compilation and installation
1 | git clone https://github.com/eclipse/eclipse.jdt.ls.git --depth 1 |
The configuration files and binaries after installation are located in the ./org.eclipse.jdt.ls.product/target/repository directory
- The runtime logs are by default in the config directory, for example, under
./org.eclipse.jdt.ls.product/target/repository/config_linux/
3.3 Color Scheme
3.3.1 gruvbox
Home: gruvbox
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Install:
1 | # ~/.vim/colors not exist by default |
3.3.2 solarized
Home: solarized
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Install:
1 | # ~/.vim/colors not exist by default |
3.3.3 catppuccin
Home: catppuccin/nvim
Configuration(~/.config/nvim/lua/packer-plugins.lua):
1 | use { "catppuccin/nvim", as = "catppuccin" } |
3.3.4 Trending Neovim Colorschemes
3.4 Dashboard
Suggest me some startup screen plugins
3.4.1 dashboard-nvim
Home: dashboard-nvim
Configuration(~/.config/nvim/lua/packer-plugins.lua):
1 | use { |
FAQ:
- It has compatible issue with LeaderF, every time use LeaderF, the bottom line go up by one line.
3.4.2 alpha-nvim
Home: alpha-nvim
Configuration(~/.config/nvim/lua/packer-plugins.lua):
1 | use { |
3.5 vim-airline
Home: vim-airline
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
3.6 lazy.nvim tools
3.6.1 noice.nvim
Home: noice.nvim
Configuration(~/.config/nvim/lua/packer-plugins.lua):
1 | use { |
3.6.2 which-key
Home: which-key
Configuration(~/.config/nvim/lua/packer-plugins.lua):
1 | use { |
3.7 indentLine
Home: indentLine
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
3.8 Highlighting
3.8.1 nvim-treesitter
Home: nvim-treesitter
Configuration(~/.config/nvim/lua/packer-plugins.lua):
1 | use { |
Usage:
:TSInstall <language_to_install>:TSInstallInfo
3.8.2 vim-cpp-enhanced-highlight
Home: vim-cpp-enhanced-highlight
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
3.9 coc.nvim
Home: coc.nvim
This plugin serves as an LSP Client and can support multiple different LSP Servers.
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
:CocStart: If auto-start is disabled in the configuration, this command needs to be run manually to start Coc.:CocUpdate: Update all plugins.:CocConfig: Edit the configuration file located at~/.vim/coc-settings.json.:CocAction: Code actions (e.g., code generation).:CocInfo:CocList [options] [args]:CocList extensions- Operations:
- Insert mode
[Ctrl] + o: Switch to normal mode
- Normal mode
i/I/o/O/a/A: Enter insert modep: Toggle preview window[Ctrl] + e: Scroll down in preview window[Ctrl] + y: Scroll up in preview window
- Insert mode
:CocCommand <plugin-command>:CocCommand workspace.showOutput: View logs
Paths:
~/.config/coc/extensions: Plugin directory
Help Doc(:help coc-nvim):
:help coc-inlayHint
FAQ:
client coc abnormal exit with: 1: Most likely an issue withnode.- The
nodeversion should neither be too new nor too old;v16is recommended. clangdversion 16 or above supports macro expansion (K).- How to modify header file search paths? Specify the
-Iparameter incompile_commands.jsonorcompile_flags.txt. - Index file path:
<project path>/.cache/clangd. - Setting
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)incmakegeneratescompile_commands.jsonwhose compile commands do not include the-std=gnu++17flag, causingclangdto warn when processing C++17 features (e.g.,Decomposition declarations are a C++17 extension (clang -Wc++17-extensions)). This can be fixed by settingCMAKE_CXX_FLAGSto add the compile flag-std=gnu++17.- Setting only
CMAKE_CXX_STANDARDis not enough; you also need to setCMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED. See CMake’s set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11) does not work.
- Setting only
- Setting
set(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER g++)incmakedoes not affectclangd. For example,clangdoes not support the-fopt-info-vecflag, and will still warn. - The standard library search path used by
clangdis determined by the compiler used in the compile commands insidecompile_commands.json. If the compiler is an older version, it will use the corresponding older header paths; a newer compiler uses newer header paths.
3.9.1 coc-explorer
Home: coc-explorer
Install:
:CocInstall coc-explorer
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
?: Help documentationj: Move cursor downk: Move cursor uph: Collapse directoryl: Expand directory or open filegh: Recursively collapse allgl: Recursively expand all*: Select/DeselectJ: Select/Deselect and move cursor downK: Select/Deselect and move cursor upIl: Enable/disable filelabelpreviewIc: Enable/disable file content previewq: Quita: Create new fileA: Create new directoryr: Renamedf/dF: Delete file;dfmoves to recycle bin,dFdeletes permanently- Symbols:
?: New file, not yet tracked bygitA: New file, added to staging areaM: File modifieddim: File differs from last commitbright: File differs from staging area
- Assorted:
- The number before the file indicates the number of errors; you can use
Ilto view the full label.
- The number before the file indicates the number of errors; you can use
3.9.2 coc-java
Home: coc-java
The LSP-Server implementation for the Java language is jdt.ls. The coc-java extension for coc.nvim provides further encapsulation of jdt.ls.
Install:
:CocInstall coc-java- Install Path:
~/.config/coc/extensions/node_modules/coc-java - Data Path:
~/.config/coc/extensions/coc-java-data
Configuration(:CocConfig)
1 | { |
Usage:
:CocCommand workspace.showOutput java: Viewjdt.lslogs"java.trace.server": "verbose": More detailed logs
:CocCommand java.open.serverLog: View rawjdt.lslogs
**Tips: **
- If the project uses third-party libraries like
thriftorprotobufthat generate source code, you need to package the generated source code and.classfiles into.jarfiles, then informjdt.lsvia configuration:-
Use the
java.project.referencedLibrariessetting to pass additional jar paths. This setting may not work properly. The issue Doesn’t recognize imports in classpath on a simple project mentions switching fromvimtoneovimcan fix this. Other related issues: -
Alternatively, configure
.classpathas per eclipse.jdt.ls/org.eclipse.jdt.ls.core/.classpath.1
2
3
4
<classpath>
<classpathentry kind="lib" path="xxx.jar" sourcepath="xxx-source"/>
</classpath> -
Assuming a submodule uses
thrift, you need to place the.classpathfile in the submodule’s directory, not in the root directory of the project.
-
- When the plugin
org.eclipse.m2e:lifecycle-mappingis present,jdt.lscannot work properly. This issue is currently unresolved.
3.9.3 coc-pyright
Home: coc-pyright
Install:
:CocInstall coc-pyright
Configuration(:CocConfig)
python.analysis.typeCheckingMode: Disable error messages likereportGeneralTypeIssues. Since Python is a dynamically typed language, errors from static type inference can be ignored.
1 | { |
**Tips: **
-
Third-party libraries installed via pip cannot be found by pyright
- You can use the venv module to create an isolated Python environment. The steps are as follows (from the
coc-pyrightofficial documentation):
1
2
3
4python3 -m venv ~/.venv
source ~/.venv/bin/activate
<install modules with pip and work with Pyright>
deactivate - You can use the venv module to create an isolated Python environment. The steps are as follows (from the
-
Format imports
CocCommand pyright.organizeimports
3.9.4 coc-rust-analyzer
Home: coc-rust-analyzer
Install:
:CocInstall coc-rust-analyzer- Make sure
rust-analyzeris installed:rustup component add rust-analyzer
3.9.5 coc-snippets
Home: coc-snippets
coc-snippets provides snippet expansion functionality (similar to sout, psvm, .var, etc. in IDEA).
Install:
:CocInstall coc-snippets- Install Path:
~/.config/coc/extensions/node_modules/coc-snippets
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
- In insert mode, after typing a snippet trigger, press
<c-e>to expand the snippet :CocList snippets: View all available snippets
FAQ:
- The latest version cannot jump to the type placeholder in
fori, so another plugin,UltiSnips, is used instead.
3.9.5.1 vim-snippets
Home: vim-snippets
The vim-snippets plugin provides a collection of snippet definitions.
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage: Same as the built-in snippets in coc-snippets
3.9.6 coc-settings.json
1 | { |
coc.preferences.diagnostic.displayByAle: Whether to display diagnostics in the style of theALEplugindiagnostic.virtualText: Whether to display diagnostic information as virtual textdiagnostic.virtualTextPrefix: Prefix for the diagnostic virtual textdiagnostic.virtualTextCurrentLineOnly: Whether to show diagnostics only for the current line where the cursor is locatedexplorer.file.reveal.auto: Automatically highlight the file corresponding to the current buffer in the file explorersuggest.noselect:true/false, indicates whether the first item is automatically selected during autocomplete. Default isfalse, meaning the first item is auto-selected; pressingtabagain moves to the second item. See Ability to tab to first optioninlayHint.display: Whether to display inlay hints by default
3.10 vimspector
Home: vimspector
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
- Layout
Variables and scopes: Top-left corner. Press Enter to expand or collapse.Watches: Middle-left. Enter edit mode, type an expression and press Enter to add a watch; use Delete key to remove a watch.StackTrace: Bottom-left corner. Press Enter to expand thread stack.Console: Standard output and standard error.
- For each project, a
.vimspector.jsonfile needs to be provided in the project root directory to configure project-related debug parametersconfigurations.<config_name>.default: true: Whether to use this configuration as default. If there are multiple configurations, do not set this.- Example for
C-Family:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34{
"configurations": {
"C-Family Launch": {
"adapter": {
"extends": "vscode-cpptools",
"sync_timeout": 100000,
"async_timeout": 100000
},
"filetypes": ["cpp", "c", "objc", "rust"],
"configuration": {
"request": "launch",
"program": "<absolute path to binary>",
"args": [],
"cwd": "<absolute working directory>",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": true,
"MIMode": "gdb"
}
},
"C-Family Attach": {
"adapter": {
"extends": "vscode-cpptools",
"sync_timeout": 100000,
"async_timeout": 100000
},
"filetypes": ["cpp", "c", "objc", "rust"],
"configuration": {
"request": "attach",
"program": "<absolute path to binary>",
"MIMode": "gdb"
}
}
}
}
3.10.1 coc-java-debug
Home: coc-java-debug
coc-java-debug depends on coc.nvim, coc-java, and vimspector
- Plugins are installed/uninstalled via
coc.nvimwith interfaces exposed throughCocCommand coc-java-debugacts as an adapter forvimspector
Installation: Run :CocInstall coc-java-debug inside the vim interface
Usage:
:CocCommand java.debug.vimspector.start- For each project, a
.vimspector.jsonfile must be provided in the project root directory to configure project-specific debug parameters:adapters.java-debug-server.port: The port number required by thejava-debug-serverat startup. This is a placeholder; a free port will be assigned automatically at runtime.configurations.<config_name>.configuration.port: The debug port number for the Java program.configurations.<config_name>.configuration.projectName: The project name corresponding topom.xml. See Debugging Java with JDB or Vim. If this parameter does not match, adding aWatchin theWatchespage will result in errors:- When not set:
Result: Cannot evaluate because of java.lang.IllegalStateException: Cannot evaluate, please specify projectName in launch.json - When set incorrectly:
Result: Cannot evaluate because of java.lang.IllegalStateException: Project <wrong name> cannot be found - Related links:
- When not set:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29{
"adapters": {
"java-debug-server": {
"name": "vscode-java",
"port": "${AdapterPort}"
}
},
"configurations": {
"Java Attach": {
"adapter": {
"extends": "java-debug-server",
"sync_timeout": 100000,
"async_timeout": 100000
},
"configuration": {
"request": "attach",
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"port": "5005",
"projectName": "${projectName}"
},
"breakpoints": {
"exception": {
"caught": "N",
"uncaught": "N"
}
}
}
}
}
3.11 Copilot.vim
Home: Copilot.vim
Getting started with GitHub Copilot
OpenAI-powered auto-completion can complete implementations based on function names.
Version requirements:
NeovimVim >= 9.0.0185
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
-
Login & Enable
1
2:Copilot setup
:Copilot enable -
:help copilot
3.12 textobj-user
Home: textobj-user
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
ia/aa: Parameter object. You can usevia/vaa/dia/daa/cia/caato select/delete/change the current parameter.ii/ai: Indentation object. You can usevii/vai/dii/dai/cii/caito select/delete/change content at the same indentation level.if/af: Function object. You can usevif/vaf/dif/daf/cif/cafto select/delete/change the current function’s content.
3.13 LeaderF
Home: LeaderF
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
- Depends
ctags
Usage:
:LeaderfFunction!: Pops up the function list:LeaderfMru: Searches recently accessed files; mapped to shortcut[Ctrl] + nvia the above configuration- File fuzzy search is mapped to shortcut
[Ctrl] + pas configured above - Search mode: start typing to perform fuzzy search
tab: Switch to normal mode; in normal mode, usej/kto move up/down<c-r>: Toggle between fuzzy search mode and regex mode<c-f>: Toggle between full path search mode and name-only search mode<c-u>: Clear search input<c-j>/<c-k>: Move cursor down/up<c-a>: Select all<c-l>: Clear selection<c-s>: Select current file<c-t>: Open selected file in a new tab<c-p>: Preview selected file
- If it doesn’t work, it might be a Python-related issue
- Run
:checkhealth
- Run
3.14 fzf.vim
Home: fzf.vim
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
- Installation additionally runs the script
~/.vim/plugged/fzf/installto download thefzfbinary. If the download is very slow or stuck, you can modify the script to use a proxy address (search for the keywordgithubin the script and add the prefixhttps://mirror.ghproxy.com/), then manually run the script to download and install.
Usage (search syntax reference: junegunn/fzf-search-syntax):
:Ag: Perform a global search (depends on the command-line toolag. Installation instructions on the plugin’s GitHub page):Rg: Perform a global search (depends on the command-line toolrg. Installation instructions on the plugin’s GitHub page)[Ctrl] + j/k/[Ctrl] + n/p: Move up/down by linePageUp/PageDown: Move up/down by page- Matching rules:
xxx: Fuzzy match (may be tokenized)'xxx: Non-fuzzy match (no tokenization)^xxx: Prefix matchxxx$: Suffix match!xxx: Inverse match- The above rules can be freely combined
- To precisely match a string containing spaces:
'Hello\ world. Since spaces are used as token separators, the space must be escaped with a backslash (\).
3.15 Git Plugins
3.15.1 vim-fugitive
Home: vim-fugitive
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
:Git: Acts as a replacement for thegitcommand; you can follow it with normalgitCLI arguments.
3.15.2 diffview.nvim
Home: diffview.nvim
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
:DiffviewOpen:DiffviewOpen HEAD~2:DiffviewOpen <commit>
3.16 nerdcommenter
Home: nerdcommenter
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
\cc: Add comment; adds comment to each line\cm: Comment the selected region with a pair of comment symbols\cs: Add a “sexy” comment\ca: Change the comment style\cu: Uncomment\c<space>: If part of the selected region is commented, uncomment the selected region; otherwise, toggle comment
3.17 vim-codefmt
Home: vim-codefmt
Supports various formatting tools:
C-Family:clang-formatCSS/Sass/SCSS/Less:js-beautifyJSON:js-beautifyHTML:js-beautifyGo:gofmtJava:google-java-format/clang-formatPython:Autopep8/Black/YAPF- Combine
isortto reorder imports. pip install autopep8 isort
- Combine
Shell:shfmt
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
:FormatCode: Format code:Glaive codefmt: View configuration (you can also see all configuration options via:help codefmt)clang_format_executable: Path to theclang_formatexecutable; can be modified with:Glaive codefmt clang_format_executable="clang-format-10"
Install the Python formatter autopep8
1 | pip install --upgrade autopep8 |
Install the Perl formatter perltidy
-
cpan install Perl::Tidy -
brew install perltidy -
The
perltidyrelated pull request has not yet been merged and needs to be manually applied: Add perl formatting support using Perltidy. Steps are as follows:1
2git fetch origin pull/227/head:pull_request_227
git rebase pull_request_227- Alternatively, if you don’t want to do that, you can temporarily replace it using the following method:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9" Configure Perl formatting; use `gg=G` to format
" https://superuser.com/questions/805695/autoformat-for-perl-in-vim
" Install perltidy via `cpan Perl::Tidy`
autocmd FileType perl setlocal equalprg=perltidy\ -st\ -ce
if has('nvim')
autocmd FileType perl nnoremap <silent><buffer> <c-l> gg=G<c-o>
else
autocmd FileType perl nnoremap <silent><buffer> <c-l> gg=G<c-o><c-o>
endif
- Alternatively, if you don’t want to do that, you can temporarily replace it using the following method:
Install the JSON formatter js-beauty
npm -g install js-beautify
3.18 vim-surround
Home: vim-surround
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
- Full usage reference:
:help surround cs:cs, change surroundings— replace the surrounding characters of the current textcs([cs[{cs{<q>cs{>
ds:ds, delete surroundings— delete the surrounding characters of the current textds{ds<ds<q>
ys:you surround— add surrounding characters to specified text. Usually used with text objectsysiw[—iwis a text objectysa"fprint—a"is the text object,fmeans surround by function call,printis the function name. Format:print(<text>)ysa"Fprint— like above,Fadds extra spaces inside parentheses:print( <text> )ysa"<c-f>print— like above,<c-f>adds the surrounding on the outermost side:(print <text>)
yss: surround the current line (excluding leading and trailing whitespace)yss(yssbyss{yssB
yS: likeys, but adds surrounding characters on the line before and after the selectionySiw[—iwis the text object
ySS: likeyss, but adds surrounding characters on the line before and after the selectionySS(ySSbySS{ySSB
[visual]S: add surrounding characters to the visually selected textvllllS'—venters visual mode,llllmoves 4 chars rightvllllSfprint— like above,fmeans surround by function call,printis the function name:print(<text>)vllllSFprint— like above,Fadds extra spaces:print( <text> )vllllS<c-f>print— like above,<c-f>adds the surrounding on the outermost side:(print <text>)
3.19 UltiSnips
Home: UltiSnips
UltiSnips is the ultimate solution for snippets in Vim.
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
3.20 vim-wordmotion
Home: vim-wordmotion
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
3.21 Complete Configuration
3.21.1 ~/.vimrc or ~/.config/nvim/init.vim
1 | " Load extra config (pre step) |
3.21.2 ~/.config/nvim/lua/packer-plugins.lua
mkdir -p ~/.config/nvim/lua
1 | vim.cmd [[packadd packer.nvim]] |
4 Legacy Plugins
These are the plugins I have eliminated.
4.1 nerdtree
Home: nerdtree
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
:NERDTreeToggle: Open the file manager.:NERDTreeFind: Open the file manager, and locate the current file.
4.2 vim-gutentags
Home: vim-gutentags
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
:GutentagsUpdate: Manually trigger tag updates.
Trouble-shooting:
let g:gutentags_define_advanced_commands = 1: Allowsgutentagsto enable some advanced commands and options- Run
:GutentagsToggleTrace: It will log the output ofctags/gtagscommands in vim’smessageloglet g:gutentags_trace = 1: Provides similar functionality
- Save the file to trigger a database update
:message: Allows you to review the message log again
FAQ:
gutentags: gtags-cscope job failed, returned: 1- Reason 1: Switching branches in a
gitrepository may cause thegtagsdbto become corrupted.gutentagsuses a command likegtags --incremental <gtagsdb-path>to update thegtagsdb, which can result in a segmentation fault. This issue manifests asgutentags: gtags-cscope job failed, returned: 1.- Solution: Modify the
gutentagssource code to remove the--incrementalparameter. Use the following command to modify it in one step:sed -ri "s|'--incremental', *||g" ~/.vim/plugged/vim-gutentags/autoload/gutentags/gtags_cscope.vim
- Solution: Modify the
- Reason 1: Switching branches in a
gutentags: ctags job failed, returned: 1- Reason 1: The installed version of ctags is too old. Reinstall a newer version.
- How to disable:
let g:gutentags_enabled = 0let g:gutentags_dont_load = 1
4.2.1 gutentags_plus
Home: gutentags_plus
Without this plugin, we typically use gtags in the following way:
set cscopeprg='gtags-cscope': Set thecscopecommand to point togtags-cscopecscope add <gtags-path>/GTAGS: Add thegtagsdbtocscopecscope find s <symbol>: Start symbol indexing
The plugin provides a command GscopeFind for gtags queries.
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Keymap Explanation:
| Keymap | Description |
|---|---|
\gd |
Find the definition of the symbol under the cursor |
\gr |
Find references to the symbol under the cursor |
\ga |
Find assignments to the symbol under the cursor |
\gt |
Find the string under the cursor |
\ge |
Search the string under the cursor using egrep pattern |
\gf |
Find the filename under the cursor |
\gi |
Find files that include the header under the cursor |
4.2.2 vim-preview
Home: vim-preview
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
- In
quickfix, presspto open the preview - In
quickfix, pressPto close the preview D: Scroll down half a page in the previewU: Scroll up half a page in the preview
4.2.3 rainbow
Home: rainbow
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
4.3 ALE
Home: ALE
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
:ALEInfo: View configuration information; scroll to the bottom to see the command execution results- How to configure
C/C++projects: DifferentC/C++projects vary greatly in structure, and there are many build tools available. As a result, it’s difficult forALEto determine the correct compilation parameters for the current file. Therefore,ALEwill try to read thecompile_commands.jsonfile in the project directory to obtain the necessary compilation parameters. - Specify the header file path for third-party libraries. The environment variable name varies for different types of compilers. Here is an example using
gccandg++:export C_INCLUDE_PATH=${C_INCLUDE_PATH}:<third party include path...>export CPLUS_INCLUDE_PATH=${CPLUS_INCLUDE_PATH}:<third party include path...>
FAQ:
- If the
linterusesgccorg++, even with syntax errors, no warning messages will appear. However, by using:ALEInfo, you can see the error messages. This happens because ALE identifies errors by the keyworderror, but in my environment,gccoutputs compilation errors in Chinese as错误. As a result, ALE does not recognize these as errors. The solution is as follows:mv /usr/share/locale/zh_CN/LC_MESSAGES/gcc.mo /usr/share/locale/zh_CN/LC_MESSAGES/gcc.mo.bakmv /usr/local/share/locale/zh_CN/LC_MESSAGES/gcc.mo /usr/local/share/locale/zh_CN/LC_MESSAGES/gcc.mo.bak
- If you cannot find the
gcc.mofile, you can use thelocatecommand to search for it.
4.4 LanguageClient-neovim
Home: LanguageClient-neovim
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Install:
- After entering the Vim interface, execute
:PlugInstall. During installation, a scriptinstall.shneeds to be executed, which downloads a binary from GitHub. In mainland China, this download may time out and fail. You can manually install it using the following method:
1 | # Assuming the project has already been downloaded locally via :PlugInstall |
Usage:
:LanguageClientStart: Since auto-start was disabled in the configuration above, you need to start it manually:LanguageClientStop: Stop the language client:call LanguageClient_contextMenu(): Open the operations menu
Keymap Explanation:
| Keymap | Description |
|---|---|
\rd |
Find the definition of the symbol under the cursor |
\rr |
Find references to the symbol under the cursor |
\rv |
View the description of the symbol under the cursor |
\rn |
Rename the symbol under the cursor |
\hb |
Find the parent class of the symbol under the cursor (ccls only) |
\hd |
Find the subclasses of the symbol under the cursor (ccls only) |
4.4.1 C-Family
4.4.1.1 clangd
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
clangd: For related configuration, refer to LanguageClient-neovim/wiki/Clangdclangdcannot change the cache storage path; by default, it uses${project}/.cacheas the cache directoryclangdsearches forcompile_commands.jsonin the path specified by the--compile-commands-dirparameter. If not found, it recursively searches in the current directory and the directories above each source file’s location
1 | call plug#begin() |
4.4.1.2 ccls
It is not recommended, as large projects consume too many resources and often freeze.
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
ccls: For related configuration, refer to ccls-project-setupcclssearches forcompile_commands.jsonin the root directory of the project
1 | call plug#begin() |
~/.vim/languageclient.json
- All paths must be absolute paths;
~cannot be used
1 | { |
4.4.2 Java-jdtls
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Create a script with the full path /usr/local/bin/jdtls containing the following content:
1 |
|
FAQ:
- Cannot access classes in the JDK and third-party libraries.
- For Maven projects, if there are additional directories in the standard directory structure, such as
<project-name>/src/main/<extra_dir>/com,jdt.lscannot automatically scan the entire project. The file will only be added to the parsing list if opened manually.
4.5 Code Completion
4.5.1 YouCompleteMe
Home: YouCompleteMe
Install:
1 | # Define a function to adjust GitHub URLs to speed up the download process. This function will be used multiple times |
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
How it worked:
- Using
compilation database: If there is acompile_commands.jsonin the current directory, it reads this file to compile and parse the code .ycm_extra_conf.py: If there is nocompilation database,ycmwill recursively search upward in the directory hierarchy for the first.ycm_extra_conf.pyfile. If none is found, it will load the global configuration (if theg:ycm_global_ycm_extra_confparameter is set)
Configure ~/.ycm_extra_conf.py, with the following content (for C/C++, applicable to most simple projects), for reference only
1 | def Settings(**kwargs): |
Usage:
- By default, only generic completion is available, such as adding already existing characters from the file to the dictionary. This way, if the same string is typed again, it will suggest completion
- For semantic completion, you can generate a
compile_commands.jsonusing build tools likecmakeand place it in the root directory of the project. Then, open the project in vim to enable semantic completion [Ctrl] + n: Next entry[Ctrl] + p: Previous entry
4.5.2 vim-javacomplete2
Home: vim-javacomplete2
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
4.6 vim-grepper
Home: vim-grepper
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
:Grepper
4.7 vim-signify
Home: vim-signify
Configuration(~/.vimrc):
1 | call plug#begin() |
Usage:
set signcolumn=yes, changed lines will be marked:SignifyDiff: compare the current file differences using a left-right split screen
5 vim-script
5.1 Tips
filereadablecannot recognize~, you need to useexpand, for examplefilereadable(expand('~/.vim/gtags.vim'))- Function names should start with an uppercase letter or with
s:. Starting with an uppercase letter means global visibility, starting withs:means script-local visibility exists('&cscopequickfix'): checks if the optioncscopequickfixexistshas('nvim'): checks if a certain feature is enabled
6 nvim
6.1 Install
1 | git clone https://github.com/neovim/neovim.git |
Or Install from Nvim development (prerelease) build (Prefer)
1 | wget https://github.com/neovim/neovim/releases/download/v0.11.2/nvim-linux-x86_64.tar.gz |
6.1.1 Node Version Management
nvm:
1 | nvm ls-remote |
1 | npm install -g n |
6.2 config path
1 | " ~/.config/nvim |
6.3 nvim share configuration of vim
nvim and vim use different directories to manage configuration files. You can share configurations by using symbolic links, as follows:
1 | # nvim's config file is ~/.config/nvim/init.vim |
6.4 Tips
- You might see an error like
Vimspector unavailable: Requires Vim compiled with +python3:- Run
:checkhealthfor a self-check, which will prompt you to installpynvim - Set
let g:python3_host_prog = '/path/to/your/python3'
- Run
- In a new environment, after installing
nvim, it’s best to runcheckhealthto verify everything, otherwise many plugins may not work properly due to missing dependencies likepython, for exampleLeaderF - Use Node.js version
16.19, which can be installed withnvm install v16.19.0
7 Tips
7.1 Large Files Run Slowly
Disable loading all plugins
1 | vim -u NONE <big file> |
7.2 Export Settings
Example 1
1 | :redir! > vim_keys.txt |
Example 2
1 | :redir! > vim_settings.txt |
7.3 Save and Exit Slowly in Large Project
Saving and exiting files is very slow in large projects. It was found to be caused by the vim-gutentags plugin and its related configuration. Add the following to the project configuration file .workspace.vim to disable it:
1 | let g:gutentags_enabled = 0 |
7.4 How to show which key I hit
- Enter normal mode.
- Type
:mapthen press<c-v>. - Type the key you wanted, then it interpreters it into the actual value.
7.5 Copy text through SSH
Note: As of Neovim 10.0 (specifically since this PR), native support for OSC52 has been added and therefore this plugin is now obsolete. Check :h clipboard-osc52 for more details.
:checkhealth clipboard: Check if there’s clipboard can be used.tmuxcan provide a default clipboard.
Item2 Config: General -> Selection -> Applications in terminal may access clipboard.
7.6 Filter through an external shell command
:%!xxd:%!hexdump -C:1,5!sort
7.7 Display Info Page
:intro
8 Reference
- 《Vim 中文速查表》
- 如何在 Linux 下利用 Vim 搭建 C/C++ 开发环境?
- Vim 8 中 C/C++ 符号索引:GTags 篇
- Vim 8 中 C/C++ 符号索引:LSP 篇
- 三十分钟配置一个顺滑如水的 Vim
- CentOS Software Repo
- 《Vim 中文版入门到精通》
- VimScript 五分钟入门(翻译)
- 使用 Vim 搭建 Java 开发环境
- 如何优雅的使用 Vim(二):插件介绍
- 打造 vim 编辑 C/C++ 环境
- Vim2021:超轻量级代码补全系统
- How To Install GCC on CentOS 7
- 8.x版本的gcc以及g++
- VIM-Plug安装插件时,频繁更新失败,或报端口443被拒绝等
- Cannot find color scheme ‘gruvbox’ #85
- 《鸟哥的Linux私房菜》
- Mac 的 Vim 中 delete 键失效的原因和解决方案
- 解决linux下vim中文乱码的方法
- vim-set命令使用
- 解決 ale 的 gcc 不顯示錯誤 | 把 gcc 輸出改成英文
- Mapping keys in Vim - Tutorial
- centos7 安装GNU GLOBAL
- The Vim/Cscope tutorial
- GNU Global manual
- Vim Buffers, Windows and Tabs — an overview